Authors
N Kerckhove, L Boudieu, G Ourties, J Bourdie
Lab
Université Clermont Auvergne, INSERM, NEURO-DOL Basics & Clinical Pharmacology of Pain, Clermont-Ferrand, France.
Journal
European Neuropsychopharmacology
Abstract
Chronic pain is a heavy burden disease. Current treatments are generally weakly effective or associated with adverse effects. New therapeutic approaches are therefore needed. Recent studies have suggested T-type calcium channels as an attractive target for the treatment of chronic pain. In this perspective, it was decided to perform a preclinical evaluation of the efficacy of ethosuximide, a T-type channel blocker used clinically as an antiepileptic, as a novel pharmacological treatment for chronic pain. Assessment of the effect of ethosuximide was thus made in both nociception and pain-related comorbidities as anxiety and depression are frequently encountered in chronic pain patients. Our results show that such symptoms occurred in three animal models of chronic pain designed to reflect traumatic neuropathic, chemotherapy-induced neuropathic and inflammatory pain conditions. Administration of ethosuximide reduced both chronic pain and comorbidities with a marked intensity ranging from partial reduction to a complete suppression of symptoms. These results make ethosuximide, and more broadly the inhibition of T-type calcium channels, a new strategy for the management of uncontrolled chronic pain, likely to improve not only pain but also the accompanying anxiety and depression.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
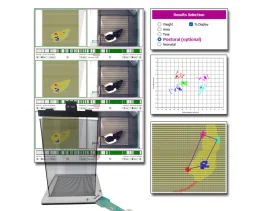
Thermal Place Preference, 2 Temperatures Choice Nociception Test (BIO-T2CT)
Keywords/Topics
Douleurs chroniques; Anxiété; Dépression; Troubles de l'humeur; Douleur
Source :
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0924977X19317249#!

 Douleur - Allodynie/Hyperalgésie Thermique
Douleur - Allodynie/Hyperalgésie Thermique Douleur - Spontanée - Déficit de Posture
Douleur - Spontanée - Déficit de Posture Douleur - Allodynie/Hyperalgésie Mécanique
Douleur - Allodynie/Hyperalgésie Mécanique Apprentissage/Mémoire - Attention - Addiction
Apprentissage/Mémoire - Attention - Addiction Physiologie & Recherche Respiratoire
Physiologie & Recherche Respiratoire


































 Douleur
Douleur Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
Système Nerveux Central (SNC)  Neurodégénérescence
Neurodégénérescence Système sensoriel
Système sensoriel Système moteur
Système moteur Troubles de l'humeur
Troubles de l'humeur Autres pathologies
Autres pathologies Système musculaire
Système musculaire Articulations
Articulations Métabolisme
Métabolisme Thématiques transversales
Thématiques transversales Congrès & Meetings 2026
Congrès & Meetings 2026 