
Les Kits contextuels pour T2CT ont été conçus pour enrichir les études de préférence de place...

Les Kits contextuels pour T2CT ont été conçus pour enrichir les études de préférence de place...

Une méthode simple pour quantifier objectivement la force musculaire des rats et souris et...

La roue d'activité spontanée BIOSEB offre une solution efficace pour quantifier l'activité...

La Roue Instrumentée pour Exercice Spontané est une méthode simple pour mesurer l'activité...

Une façon simple pour mesurer l'activité des rongeurs sur plusieurs jours dans leurs cages de...

Conçu pour les études sur l'entraînement physique et la fatigue chez les rongeurs - et désormais...

Instrument de test de la sensibilité de l'animal à la douleur résultant de l'exposition à la...

Un test indépendant de l'opérateur pour étudier les seuils de douleur chez les rongeurs (rats et...

Le Test de Gradient Thermique indépendant de l'opérateur est un nouvel instrument de recherche...

Les Kits contextuels pour T2CT ont été conçus pour enrichir les études de préférence de place...

Un système permettant l'analyse de la posture des animaux par la répartition du poids sur...

Test non douloureux pour mesurer le niveau d'inconfort (incapacitance) de petits animaux comme...

Un instrument unique qui ne fournit pas seulement la mesure indépendante et automatisée du poids...
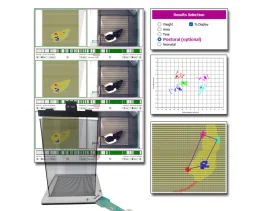
Étendez votre analyse grâce à des calculs posturaux et locomoteurs avancés Le système de...

Une solution rapide pour déterminer le seuil de sensibilité à la douleur mécanique chez les...

En tant que version électronique du classique esthésiomètre à filaments de Von Frey, la...

Nouvelles cage de contention modulables ROBUSTES pour maintenir doucement les rongeurs (rats et...

Une solution économique et versatile pour les situations nécessitant des tests sensoriels...

Dédié aux petits animaux tels que les rats et les souris, le Smalgo est un algomètre (ou...

La version 5 du Test de Suspension Caudale de Bioseb, basée sur des capteurs de force ainsi que...

NOUVEAU ! Solution complète (matériel et logiciel), dédiée et automatisée pour le Labyrinthe...

Un nouveau système innovant pour l'automatisation du test d'Open Field pour rats et souris:...

Test open-field - ARENE UNIQUEMENT utilisé pour évaluer l'activité basale des rongeurs (rats et...

Le nouveau Test de Nage Forcée Bioseb DUAL SENSOR à été développé selon une double approche: En...

Un nouveau système innovant pour l'automatisation du test de Reconnaissance d'Object ("Novel...

Test open-field - ARENE UNIQUEMENT utilisé pour évaluer l'activité basale des rongeurs (rats et...

Un système expérimental d'enclos entièrement modulable conçu pour conduire des procédures de...

Appareil d'utilisation très simple pour souris Possibilité de sortir les données sur PC

Une chambre expérimentale standard pour l'évaluation automatisée ou manuelle de la préférence de...
Mesures des paramètres physiologique en temps réel chez le rats - non invasive et sans aucune...

L'ETH-401 est un amplificateur de pont pour différents transducteurs qui fournit quatre canaux...

Le IX-118 est un système d'acquisition de données rapide 100 kHz à haute résolution et approprié...

L'ETH-256 est un amplificateur 2 canaux haute performance à usage général de la recherche en...

Stimulateur à canaux multiples toutes options pour stimulation neuro-musculaire

Découvrez BIO-FOODIS, la solution de nouvelle génération pour comprendre le comportement...

Système modulaire permettant l'intégration du métabolisme respiratoire, de l'apport de...

Équipements innovants et appropriés pour mesurer la consommation de nourriture / boisson ainsi...

Un analyseur d'oxygène et de dioxyde de carbone économique, de haute performance avec des taux...
Un système permettant l'analyse de la posture des animaux par la répartition du poids sur chacune des 4 pattes. Le DWB est un test unique dans l'étude de nombreux modèles de douleurs, principalement non évoquée , neuropathique ou encore inflammatoire ainsi que pour les études sur l'osthéoarthrite et divers affections du SNC.
Le nouvelle version DWB2 intègre une nouvelle interface logiciel plus simple avec gestion des listes d'animaux ainsi que de nouveaux algorithmes d'analyse automatique de la posture.
![]()
![]()
![]() Historique
Historique
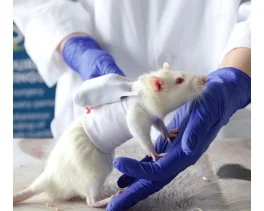
• 2006 - Test d'Incapacitance / Distribution Pondérale Statique: Premier test de mesure de la douleur spontanée utilisé en analgésie/nociception. L’appareil permet la mesure de la répartition du poids d’un rongeur en contention sur ses pattes arrières.
• 2008 - Test de Distribution Pondérale Dynamique Basique: L’instrument permet la mesure de la répartition du poids de l’animal sur ses 4 pattes et permet de s’affranchir de la contention.
• 2011 - Test de Distribution Pondérale Dynamique Avancé: Nouvelle version logiciel du DWB permettant le suivi vidéo de l’animal afin d’automatiser une partie du test.
• 2018 - Test de Distribution Pondérale Dynamique 2.0: Nouveau logiciel en 3 onglets avec performances d’automatisations améliorées et intégration de nouvelles fonctionnalités majeures.![]() Présentation
Présentation
Pour des raisons éthiques et afin d’étudier le niveau d’inconfort ou douleur non-évoquée des rongeurs, des tests permettant l’évaluation de la douleur sans provoquer de stimulus sur les animaux ont été développés. Ces tests dits « d’incapacitance » permettent la mesure de la répartition du poids sur les 2 pattes arrière des rongeurs en contention, impliquant un niveau de stress élevé pour les animaux.
Depuis son lancement en 2008, le test de distribution pondérale dynamique DWB est le seul test d’évaluation de la douleur non évoquée des rongeurs permettant de s’affranchir de cette contention des animaux. Il est aussi le seul instrument capable de mesurer avec précision l’évolution de la posture des rongeurs par la mesure de répartition du poids sur chacune de leurs 4 pattes.
Ainsi, le DWB permet de travailler avec des animaux libres de leurs déplacements dans une arène de dimensions adaptées aux rats ou à la souris. Cela permet de réduire considérablement le niveau de stress lié à la contention de l’animal et d’améliorer ainsi la fiabilité des résultats.
Validé par plus d’une trentaine de publications, cet instrument a permis de répondre à de nombreuses interrogations dans les modèles de douleurs non évoquées, neuropathiques, inflammatoires ou encore osthéoartritiques. Plus récemment, le cadre d’utilisation du DWB a dépassé les modèles de douleur et l’analyse de la posture s’est avéré idéale pour l’étude de troubles osseux (fractures, cancers, arthrose..), de différents problèmes du système nerveux central (ischémies) ou encore du système vestibulaire (vertige).![]() Principe de fonctionnement
Principe de fonctionnement
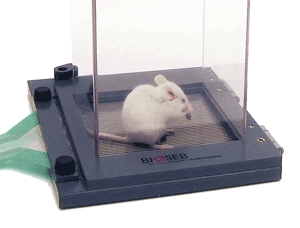
L’animal est placé dans la cage du DWB (Dynamic Weight Bearing) sur une durée d’environ 5 minutes.
Durant le test, le DWB couple l’utilisation de deux technologies :
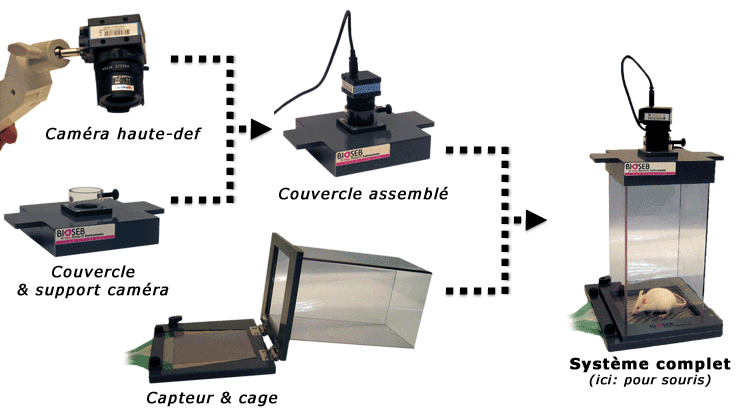
• Une matrice d’environ 2000 capteurs de force de grande précision (0.02g chez la souris et 0.15g chez la souris) : Cette matrice constitue le sol de la cage sur lequel l’animal évolue librement. Les capteurs permettent la mesure en grammes de la répartition du poids des animaux sur chacune de leurs 4 pattes. L’appareil utilise spécifiquement des capteurs pour rats ou pour souris avec un niveau de sensibilité adapté (de 0 à 4g chez la souris et de 0 à 40g chez le rats).
• Un suivi vidéo de l’animal : L’animal est filmé par-dessus grâce à une caméra haute résolution. La vidéo est analysée en temps réel lors du test par un logiciel de tracking permettant une analyse précise de la morphologie de l’animal.
Le logiciel est donc capable d’analyser précisément la position de l’animal durant l’ensemble du test afin d’identifier automatiquement la position des 4 pattes sur les capteurs de force.
L’acquisition des informations provenant des capteurs de force et de la caméra se faisant à haute fréquence (30 htz), le DWB est capable d’analyser les changements de positions rapides des animaux permettant des mesures complètes afin d’analyser précisément l’évolution de la posture des animaux immobiles ou en mouvements.
![]() Versions et installation
Versions et installation
Nous proposons un passage vers la nouvelle version pour les utilisateurs du DWB1. Votre matériel actuel est parfaitement compatible et seule une mise à jour du logiciel sera nécessaire.
Vos acquisitions faites avec le DWB1 pourront être analysées avec le nouveau DWB2 afin de bénéficier de l’interface et de la puissance d’analyse du nouveau logiciel.
Le DWB avancé est disponible en 3 versions: RAT (BIO-DWB-AUTO-R), SOURIS (BIO-DWB-AUTO-M), COMBO RAT-SOURIS (BIO-DWB-AUTO-DU).
Fiche technique
Array
(
[2014] => Array
(
[id] => 2014
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Integrating-sensitive-motor-tasks-with-histopathology-detects-sex-differences-in-recovery-after-spinal-cord-injury-n2014
[title] => Integrating sensitive motor tasks with histopathology detects sex differences in recovery after spinal cord injury
[paragraph_crop] => Integrating sensitive motor tasks with histopathology detects sex differences in recovery [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-12-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[39] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 39
[title] => Moelle épinière
[link_rewrite] => Moelle-epiniere
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2016] => Array
(
[id] => 2016
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Sensory-Deficits-in-mice-with-Lateral-Spinal-Cord-Hemisection-Mimic-the-Brown-Sequard-Syndrome-n2016
[title] => Sensory Deficits in mice with Lateral Spinal Cord Hemisection Mimic the Brown-Sequard Syndrome
[paragraph_crop] => Sensory Deficits in mice with Lateral Spinal Cord Hemisection Mimic the Brown-Sequard Syndrome
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-09-11 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[39] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 39
[title] => Moelle épinière
[link_rewrite] => Moelle-epiniere
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2012] => Array
(
[id] => 2012
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/The-mRNA-Translation-Inhibitor-Vioprolide-A-Prevents-Inflammatory-Pain-Like-Behaviour-With-Limited-Action-on-Already-Established-Pain-Like-Behaviour-in-Mice-n2012
[title] => The mRNA Translation Inhibitor Vioprolide A Prevents Inflammatory Pain-Like Behaviour With Limited Action on Already Established Pain-Like Behaviour in Mice
[paragraph_crop] => The mRNA Translation Inhibitor Vioprolide A Prevents Inflammatory Pain-Like Behaviour With [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-09-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[96] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 96
[title] => Autres pathologies
[link_rewrite] => Autres-pathologies
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2015] => Array
(
[id] => 2015
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/The-effect-of-a-low-transition-temperature-mixture-for-enhanced-bioavailability-of-celecoxib-in-combination-with-hyaluronic-acid-in-a-rat-model-with-post-traumatic-knee-osteoarthritis-n2015
[title] => The effect of a low transition temperature mixture for enhanced bioavailability of celecoxib in combination with hyaluronic acid in a rat model with post-traumatic knee osteoarthritis
[paragraph_crop] => The effect of a low transition temperature mixture for enhanced bioavailability of celecoxib [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-08-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2013] => Array
(
[id] => 2013
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/5-HT2C-agonism-as-a-neurotherapeutic-for-sarcopenia--preclinical-proof-of-concept-n2013
[title] => 5-HT2C agonism as a neurotherapeutic for sarcopenia- preclinical proof of concept
[paragraph_crop] => 5-HT2C agonism as a neurotherapeutic for sarcopenia- preclinical proof of concept
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-06-19 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[63] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 63
[title] => Système musculaire général
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-musculaire-general
)
)
)
[2008] => Array
(
[id] => 2008
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Extensive-Periosteal-Injury-During-Fracture-Induces-Long-Term-Pain-in-Mice-n2008
[title] => Extensive Periosteal Injury During Fracture Induces Long-Term Pain in Mice
[paragraph_crop] => Extensive Periosteal Injury During Fracture Induces Long-Term Pain in Mice
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-06-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[75] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 75
[title] => Fractures
[link_rewrite] => Fractures
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2011] => Array
(
[id] => 2011
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/PAIN-n2011
[title] => PAIN
[paragraph_crop] => PAIN
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-05-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2009] => Array
(
[id] => 2009
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Chronic-pain-increases-sensitivity-to-pain-induced-reinstatement-of-ethanol-seeking-in-male-mice-n2009
[title] => Chronic pain increases sensitivity to pain-induced reinstatement of ethanol seeking in male mice
[paragraph_crop] => Chronic pain increases sensitivity to pain-induced reinstatement of ethanol seeking in male mice
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-01-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2010] => Array
(
[id] => 2010
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/AAV-mediated-overexpression-of-Prdm12-in-knee-innervating-afferents-reduces-inflammatory-joint-pain-and-neuronal-hyperexcitability-in-mice-n2010
[title] => AAV-mediated overexpression of Prdm12 in knee-innervating afferents reduces inflammatory joint pain and neuronal hyperexcitability in mice
[paragraph_crop] => AAV-mediated overexpression of Prdm12 in knee-innervating afferents reduces inflammatory joint [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-01-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1909] => Array
(
[id] => 1909
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/myostatin-and-cxcl11-promote-nervous-tissue-macrophages-to-maintain-osteoarthritis-pain-n1909
[title] => Myostatin and CXCL11 promote nervous tissue macrophages to maintain osteoarthritis pain
[paragraph_crop] => Myostatin and CXCL11 promote nervous tissue macrophages to maintain osteoarthritis pain
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2024-02-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1906] => Array
(
[id] => 1906
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/stomatin-like-protein-3-modulates-the-responses-of-a--but-not-c-fiber-bone-afferent-neurons-to-noxious-mechanical-stimulation-in-an-animal-model-of-acute-experimental-bone-pain-n1906
[title] => Stomatin-like protein 3 modulates the responses of Aδ- but not C fiber bone afferent neurons to noxious mechanical stimulation in an animal model of acute experimental bone pain
[paragraph_crop] => Stomatin-like protein 3 modulates the responses of Aδ- but not C fiber bone afferent neurons [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2023-12-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1884] => Array
(
[id] => 1884
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/advanced-dynamic-weight-bearing-as-an-observer-independent-measure-of-hyperacute-hypersensitivity-in-mice-n1884
[title] => Advanced Dynamic Weight Bearing as an Observer-independent Measure of Hyperacute Hypersensitivity in Mice
[paragraph_crop] => Advanced Dynamic Weight Bearing as an Observer-independent Measure of Hyperacute [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2023-08-21 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1850] => Array
(
[id] => 1850
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/inflammation-and-subsequent-nociceptor-sensitization-in-the-bone-marrow-are-involved-in-an-animal-model-of-osteoarthritis-pain-n1850
[title] => Inflammation and subsequent nociceptor sensitization in the bone marrow are involved in an animal model of osteoarthritis pain
[paragraph_crop] => Inflammation and subsequent nociceptor sensitization in the bone marrow are involved in an [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2023-05-03 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1552] => Array
(
[id] => 1552
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/objective-and-quantitative-evaluation-of-spontaneous-pain-like-behaviors-using-dynamic-weight-bearing-system-in-mouse-models-of-postsurgical-pain-n1552
[title] => Objective and Quantitative Evaluation of Spontaneous Pain-Like Behaviors Using Dynamic Weight-Bearing System in Mouse Models of Postsurgical Pain
[paragraph_crop] => Objective and Quantitative Evaluation of Spontaneous Pain-Like Behaviors Using Dynamic [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-06-02 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[34] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 34
[title] => Douleurs spontanées
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-spontanées
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1558] => Array
(
[id] => 1558
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/comprehensive-evaluation-of-long-term-dynamic-mechanical-behavior-in-a-rat-mia-oa-model-n1558
[title] => Comprehensive Evaluation of Long-term Dynamic Mechanical Behavior in a Rat MIA OA Model
[paragraph_crop] => Comprehensive Evaluation of Long-term Dynamic Mechanical Behavior in a Rat MIA OA Model
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-05-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1515] => Array
(
[id] => 1515
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/experimental-arthritis-inhibits-adult-hippocampal-neurogenesis-in-mice-n1515
[title] => Experimental Arthritis Inhibits Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Mice
[paragraph_crop] => Experimental Arthritis Inhibits Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Mice
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-02-24 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1497] => Array
(
[id] => 1497
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/l-thyroxine-improves-vestibular-compensation-in-a-rat-model-of-acute-peripheral-vestibulopathy-cellular-and-behavioral-aspects-n1497
[title] => L-Thyroxine Improves Vestibular Compensation in a Rat Model of Acute Peripheral Vestibulopathy Cellular and Behavioral Aspects
[paragraph_crop] => L-Thyroxine Improves Vestibular Compensation in a Rat Model of Acute Peripheral [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-02-16 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[49] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 49
[title] => Système vestibulaire
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-vestibulaire
)
)
)
[1508] => Array
(
[id] => 1508
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/intravenous-administration-of-human-mesenchymal-stem-cells-derived-from-adipose-tissue-and-umbilical-cord-improves-neuropathic-pain-via-suppression-of-neuronal-damage-and-anti-inflammatory-actions-in-rats-n1508
[title] => Intravenous administration of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue and umbilical cord improves neuropathic pain via suppression of neuronal damage and anti-inflammatory actions in rats
[paragraph_crop] => Intravenous administration of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue and [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-02-14 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1503] => Array
(
[id] => 1503
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/selenophosphate-synthetase-1-deficiency-exacerbates-osteoarthritis-by-dysregulating-redox-homeostasis-n1503
[title] => Selenophosphate synthetase 1 deficiency exacerbates osteoarthritis by dysregulating redox homeostasis
[paragraph_crop] => Selenophosphate synthetase 1 deficiency exacerbates osteoarthritis by dysregulating redox [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-02-09 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1452] => Array
(
[id] => 1452
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/sensorimotor-rehabilitation-promotes-vestibular-compensation-in-a-rodent-model-of-acute-peripheral-vestibulopathy-by-promoting-microgliogenesis-in-the-deafferented-vestibular-nuclei-n1452
[title] => Sensorimotor Rehabilitation Promotes Vestibular Compensation in a Rodent Model of Acute Peripheral Vestibulopathy by Promoting Microgliogenesis in the Deafferented Vestibular Nuclei
[paragraph_crop] => Sensorimotor Rehabilitation Promotes Vestibular Compensation in a Rodent Model of Acute [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-11-29 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[49] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 49
[title] => Système vestibulaire
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-vestibulaire
)
)
)
[1458] => Array
(
[id] => 1458
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/inhibiting-endocytosis-in-cgrp-nociceptors-attenuates-inflammatory-pain-like-behavior-n1458
[title] => Inhibiting endocytosis in CGRP nociceptors attenuates inflammatory pain-like behavior
[paragraph_crop] => Inhibiting endocytosis in CGRP nociceptors attenuates inflammatory pain-like behavior
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-10-04 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1440] => Array
(
[id] => 1440
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/weight-bearing-as-a-measure-of-disease-progression-in-experimental-autoimmune-encephalomyelitis-n1440
[title] => Weight bearing as a measure of disease progression in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
[paragraph_crop] => Weight bearing as a measure of disease progression in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-10-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[98] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 98
[title] => Maladies auto-immunes
[link_rewrite] => Maladies-auto-immunes
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[68] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 68
[title] => Scléroses multiples
[link_rewrite] => Scleroses-multiples
)
)
)
[1455] => Array
(
[id] => 1455
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/dorsal-root-ganglia-macrophages-maintain-osteoarthritis-pain-n1455
[title] => Dorsal Root Ganglia Macrophages Maintain Osteoarthritis Pain
[paragraph_crop] => Dorsal Root Ganglia Macrophages Maintain Osteoarthritis Pain
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-09-29 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1404] => Array
(
[id] => 1404
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/oral-supplementation-with-fish-cartilage-hydrolysate-accelerates-joint-function-recovery-in-rat-model-of-traumatic-knee-osteoarthritis-n1404
[title] => Oral supplementation with fish cartilage hydrolysate accelerates joint function recovery in rat model of traumatic knee osteoarthritis
[paragraph_crop] => Oral supplementation with fish cartilage hydrolysate accelerates joint function recovery in [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-04-10 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1395] => Array
(
[id] => 1395
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/alpha1antitrypsin-reduces-inflammation-and-exerts-chondroprotection-in-arthritis-n1395
[title] => Alpha_1_antitrypsin reduces inflammation and exerts chondroprotection in arthritis
[paragraph_crop] => Alpha_1_antitrypsin reduces inflammation and exerts chondroprotection in arthritis
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-02-09 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1377] => Array
(
[id] => 1377
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/comparative-study-of-anti-gouty-arthritis-effects-of-sam-myo-whan-according-to-extraction-solvents--n1377
[title] => Comparative Study of Anti-Gouty Arthritis Effects of Sam-Myo-Whan according to Extraction Solvents
[paragraph_crop] => Comparative Study of Anti-Gouty Arthritis Effects of Sam-Myo-Whan according to Extraction Solvents
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-02-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1333] => Array
(
[id] => 1333
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/mechanistic-insights-into-the-role-of-the-chemokine-ccl2-and-ccr2-axis-in-dorsal-root-ganglia-to-peripheral-inflammation-and-pain-hypersensitivity-n1333
[title] => Mechanistic Insights Into the Role of the Chemokine CCL2 and CCR2 Axis in Dorsal Root Ganglia to Peripheral Inflammation and Pain Hypersensitivity
[paragraph_crop] => Mechanistic Insights Into the Role of the Chemokine CCL2/CCR2 Axis in Dorsal Root Ganglia to [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-10-25 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1304] => Array
(
[id] => 1304
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/pain-responses-to-protease-activated-receptor-2-stimulation-in-the-spinal-cord-of-naive-and-arthritic-rats-n1304
[title] => Pain Responses to Protease-Activated Receptor-2 Stimulation in the Spinal Cord of Naive and Arthritic Rats
[paragraph_crop] => Pain Responses to Protease-Activated Receptor-2 Stimulation in the Spinal Cord of Na•ve and A [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-09-16 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[39] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 39
[title] => Moelle épinière
[link_rewrite] => Moelle-epiniere
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1472] => Array
(
[id] => 1472
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/rheumatoid-pain-models-in-rodents-and-the-application-of-dynamic-weight-bearing-test-n1472
[title] => Rheumatoid pain models in rodents and the application of dynamic weight-bearing test
[paragraph_crop] => Rheumatoid pain models in rodents and the application of dynamic weight-bearing test
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-08-26 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1302] => Array
(
[id] => 1302
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/assessment--quantification--and-management-of-fracture-pain--from-animals-to-the-clinic-n1302
[title] => Assessment- Quantification- and Management of Fracture Pain- from Animals to the Clinic
[paragraph_crop] => Assessment, Quantification, and Management of Fracture Pain: from Animals to the Clinic
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-08-22 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1289] => Array
(
[id] => 1289
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/pain-behaviour-assessments-by-gait-and-weight-bearing-in-surgically-induced-osteoarthritis-and-inflammatory-arthritis-n1289
[title] => Pain behaviour assessments by gait and weight bearing in surgically induced osteoarthritis and inflammatory arthritis
[paragraph_crop] => Pain behaviour assessments by gait and weight bearing in surgically induced osteoarthritis and [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-07-15 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1279] => Array
(
[id] => 1279
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/rab27a-contributes-to-the-processing-of-inflammatory-pain-in-mice-n1279
[title] => Rab27a Contributes to the Processing of Inflammatory Pain in Mice
[paragraph_crop] => Rab27a Contributes to the Processing of Inflammatory Pain in Mice
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-06-18 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
)
)
[1271] => Array
(
[id] => 1271
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/the-use-of-the-dynamic-weight-bearing-test-to-assess-the-effects-of-acute--intramuscularly-administered-botulinum-neurotoxin-type-a1-in-rats-n1271
[title] => The use of the dynamic weight bearing test to assess the effects of acute- intramuscularly administered botulinum neurotoxin type A1 in rats
[paragraph_crop] => The use of the dynamic weight bearing test to assess the effects of acute, intramuscularly [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-05-23 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
[94] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 94
[title] => Toxicologie
[link_rewrite] => Toxicologie
)
)
)
[1269] => Array
(
[id] => 1269
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/pain-relief-devoid-of-opioid-side-effects-following-central-action-of-a-silylated-neurotensin-analog-n1269
[title] => Pain relief devoid of opioid side effects following central action of a silylated neurotensin analog
[paragraph_crop] => Pain relief devoid of opioid side effects following central action of a silylated neurotensin analog
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-05-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1267] => Array
(
[id] => 1267
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/reg-o3-chimeric-peptide-combining-growth-hormone-and-somatostatin-sequences-improves-joint-function-and-prevents-cartilage-degradation-in-rat-model-of-traumatic-knee-osteoarthritis-n1267
[title] => REG-O3 chimeric peptide combining growth hormone and somatostatin sequences improves joint function and prevents cartilage degradation in rat model of traumatic knee osteoarthritis
[paragraph_crop] => REG-O3 chimeric peptide combining growth hormone and somatostatin sequences improves joint [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-04-14 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[35] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 35
[title] => Douleurs émotionnelles
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-émotionnelles
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1263] => Array
(
[id] => 1263
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/apamin-from-bee-venom-suppresses-inflammation-in-a-murine-model-of-gouty-arthritis-n1263
[title] => Apamin from bee venom suppresses inflammation in a murine model of gouty arthritis
[paragraph_crop] => Apamin from bee venom suppresses inflammation in a murine model of gouty arthritis
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-04-11 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1225] => Array
(
[id] => 1225
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/intra-articular-aav-php--s-mediated-chemogenetic-targeting-of-knee-innervating-drg-neurons-alleviates-inflammatory-pain-in-mice-n1225
[title] => Intra-articular AAV-PHP- S mediated chemogenetic targeting of knee-innervating DRG neurons alleviates inflammatory pain in mice
[paragraph_crop] => Intra-articular AAV-PHP. S mediated chemogenetic targeting of knee-innervating DRG neurons [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-03-31 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1253] => Array
(
[id] => 1253
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/mimicking-sampsons-retrograde-menstrual-theory-in-rats--a-new-rat-model-for-ongoing-endometriosis-associated-pain-n1253
[title] => Mimicking Sampson's Retrograde Menstrual Theory in Rats- A New Rat Model for Ongoing Endometriosis-Associated Pain
[paragraph_crop] => Mimicking Sampson's Retrograde Menstrual Theory in Rats: A New Rat Model for Ongoing [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-03-27 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[32] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 32
[title] => Douleurs abdominales, ovaro-pelviennes et liées à l'endométriose
[link_rewrite] => douleurs-abdominales-ovaro-pelviennes-et-liees-a-l-endometriose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1252] => Array
(
[id] => 1252
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/total-knee-arthroplasty-with-a-ti6al4v-and-peek-prosthesis-on-an-osteoarthritis-rat-model--behavioral-and-neurophysiological-analysis-n1252
[title] => Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Ti6Al4V and PEEK Prosthesis on an Osteoarthritis Rat Model- Behavioral and Neurophysiological Analysis
[paragraph_crop] => Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Ti6Al4V/PEEK Prosthesis on an Osteoarthritis Rat Model: [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-03-24 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1217] => Array
(
[id] => 1217
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/redox-regulation-of-soluble-epoxide-hydroxylase-does-not-affect-pain-behavior-in-mice-n1217
[title] => Redox regulation of soluble epoxide hydroxylase does not affect pain behavior in mice
[paragraph_crop] => Redox regulation of soluble epoxide hydroxylase does not affect pain behavior in mice
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-01-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1195] => Array
(
[id] => 1195
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/pain-and-knee-damage-in-male-and-female-mice-in-the-medial-meniscal-transection-induced-osteoarthritis-pain-and-knee-damage-in-male-and-female-mice-in-the-medial-meniscal-transection-induced-osteoarthritis-n1195
[title] => Pain and knee damage in male and female mice in the medial meniscal transection-induced osteoarthritis Pain and knee damage in male and female mice in the medial meniscal transection-induced osteoarthritis
[paragraph_crop] => Pain and knee damage in male and female mice in the medial meniscal transection-induced [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-12-10 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1141] => Array
(
[id] => 1141
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/spinal-microglia-contribute-to-cancer-induced-pain-through-system-xc-mediated-glutamate-release-n1141
[title] => Spinal microglia contribute to cancer-induced pain through system xC_-mediated glutamate release
[paragraph_crop] => Spinal microglia contribute to cancer-induced pain through system xC_-mediated glutamate release
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-06-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[90] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 90
[title] => Cancer
[link_rewrite] => Cancer
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[1136] => Array
(
[id] => 1136
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/yokukansan-alleviates-cancer-pain-by-suppressing-matrix-metalloproteinase-9-in-a-mouse-bone-metastasis-model-n1136
[title] => Yokukansan Alleviates Cancer Pain by Suppressing Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 in a Mouse Bone Metastasis Model
[paragraph_crop] => Yokukansan Alleviates Cancer Pain by Suppressing Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 in a Mouse Bone [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-05-26 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[90] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 90
[title] => Cancer
[link_rewrite] => Cancer
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[1127] => Array
(
[id] => 1127
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/narciclasine-exerts-anti-inflammatory-actions-by-blocking-leukocyteendothelial-cell-interactions-and-down-regulation-of-the-endothelial-tnf-receptor-1-n1127
[title] => Narciclasine exerts anti-inflammatory actions by blocking leukocyteÐendothelial cell interactions and down-regulation of the endothelial TNF receptor 1
[paragraph_crop] => Narciclasine exerts anti-inflammatory actions by blocking leukocyteÐendothelial cell [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-04-24 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[93] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 93
[title] => Inflammation
[link_rewrite] => Inflammation
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[1125] => Array
(
[id] => 1125
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/intra-articular-treatment-with-triamcinolone-acetonide-loaded-liposomes-in-the-rat-high-fat-diet-groove-model-n1125
[title] => Intra-articular treatment with triamcinolone acetonide-loaded liposomes in the rat high-fat diet groove model
[paragraph_crop] => Intra-articular treatment with triamcinolone acetonide-loaded liposomes in the rat high-fat [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-04-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1110] => Array
(
[id] => 1110
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/intra-articular-injection-of-triamcinolone-acetonide-releasing-biomaterial-microspheres-inhibits-pain-and-inflammation-in-an-acute-arthritis-model-n1110
[title] => Intra-articular injection of triamcinolone acetonide releasing biomaterial microspheres inhibits pain and inflammation in an acute arthritis model
[paragraph_crop] => Intra-articular injection of triamcinolone acetonide releasing biomaterial microspheres [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-03-07 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1107] => Array
(
[id] => 1107
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/applicability-of-a-modied-rat-model-of-acute-arthritis-for-long-term-testing-of-drug-delivery-systems-n1107
[title] => Applicability of a Modi_ed Rat Model of Acute Arthritis for Long-Term Testing of Drug Delivery Systems
[paragraph_crop] => Applicability of a Modi_ed Rat Model of Acute Arthritis for Long-Term Testing of Drug Delivery [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-02-07 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[99] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 99
[title] => Infection
[link_rewrite] => Infection
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1100] => Array
(
[id] => 1100
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/sequential-alteration-of-microglia-and-astrocytes-in-the-rat-thalamus-following-spinal-nerve-ligation-n1100
[title] => Sequential alteration of microglia and astrocytes in the rat thalamus following spinal nerve ligation
[paragraph_crop] => Sequential alteration of microglia and astrocytes in the rat thalamus following spinal nerve [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-12-20 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1097] => Array
(
[id] => 1097
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/the-analgesic-effect-of-intraarticular-onabotulinumtoxina-in-a-female-murine-model-of-collagenase-induced-chronic-degenerative-monoarthritis-n1097
[title] => The analgesic effect of intraarticular OnabotulinumtoxinA in a female murine model of collagenase induced chronic degenerative monoarthritis
[paragraph_crop] => The analgesic effect of intraarticular OnabotulinumtoxinA in a female murine model of [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-11-22 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1056] => Array
(
[id] => 1056
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/evaluation-of-neurobehavioral-impairment-in-methylmercurytreated-kkay-mice-by-dynamic-weightbearing-test-n1056
[title] => Evaluation of neurobehavioral impairment in methylmercury_treated KK_Ay mice by dynamic weight_bearing test
[paragraph_crop] => Evaluation of neurobehavioral impairment in methylmercury_treated KK_Ay mice by dynamic [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-09-02 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
[94] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 94
[title] => Toxicologie
[link_rewrite] => Toxicologie
)
)
)
[1054] => Array
(
[id] => 1054
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/microglial-pannexin-1-channel-activation-is-a-spinal-determinant-of-joint-pain-n1054
[title] => Microglial pannexin-1 channel activation is a spinal determinant of joint pain
[paragraph_crop] => Microglial pannexin-1 channel activation is a spinal determinant of joint pain
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-08-08 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1053] => Array
(
[id] => 1053
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/investigation-of-lake-hzvz-mineral-water-balneotherapy-and-hzvz-mud-treatment-in-murine-osteoarthritis-and-rheumatoid-arthritis-models-n1053
[title] => Investigation of Lake Hzvz Mineral Water Balneotherapy and Hzvz Mud Treatment in Murine Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
[paragraph_crop] => Investigation of Lake HŽv’z Mineral Water Balneotherapy and HŽv’z Mud Treatment in Murine Osteo [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-08-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[98] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 98
[title] => Maladies auto-immunes
[link_rewrite] => Maladies-auto-immunes
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1028] => Array
(
[id] => 1028
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/functional-effects-of-trka-inhibition-on-system-xc-mediated-glutamate-release-and-cancer-induced-bone-pain-n1028
[title] => Functional effects of TrkA inhibition on system xC_-mediated glutamate release and cancer-induced bone pain
[paragraph_crop] => Functional effects of TrkA inhibition on system xC_-mediated glutamate release and [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-05-05 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[90] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 90
[title] => Cancer
[link_rewrite] => Cancer
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[1065] => Array
(
[id] => 1065
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/anterior-cingulate-cortex-connectivity-is-associated-with-suppression-of-behavior-in-a-rat-model-of-chronic-pain--n1065
[title] => Anterior cingulate cortex connectivity is associated with suppression of behavior in a rat model of chronic pain-
[paragraph_crop] => Anterior cingulate cortex connectivity is associated with suppression of behavior in a rat [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-05-04 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1026] => Array
(
[id] => 1026
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/motivational-changes-that-develop-in-a-mouse-model-of-inflammation-induced-depression-are-independent-of-indoleamine-2--3-dioxygenase--n1026
[title] => Motivational changes that develop in a mouse model of inflammation-induced depression are independent of indoleamine 2- 3 dioxygenase-
[paragraph_crop] => Motivational changes that develop in a mouse model of inflammation-induced depression are [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-04-27 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[57] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 57
[title] => Dépression
[link_rewrite] => Depression
)
[93] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 93
[title] => Inflammation
[link_rewrite] => Inflammation
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
[15] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 15
[title] => Troubles de l'humeur
[link_rewrite] => Troubles-de-l-humeur
)
)
)
[1012] => Array
(
[id] => 1012
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/modulation-of-the-ngftrka-pathway-for-treatment-of-joint-pain--preclinical-in-vivo-evaluation-in-mice-n1012
[title] => Modulation of the NGF–TRKA pathway for treatment of joint pain- preclinical in vivo evaluation in mice
[paragraph_crop] => Modulation of the NGF–TRKA pathway for treatment of joint pain: preclinical in vivo evaluation [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-04-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[34] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 34
[title] => Douleurs spontanées
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-spontanées
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[963] => Array
(
[id] => 963
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/evaluation-of-the-novel-avocado-and-soybean-unsaponifiable-arthrocen-to-alter-joint-pain-and-inflammation-in-a-rat-model-of-osteoarthritis-n963
[title] => Evaluation of the novel avocado and soybean unsaponifiable Arthrocen to alter joint pain and inflammation in a rat model of osteoarthritis
[paragraph_crop] => Evaluation of the novel avocado/soybean unsaponifiable Arthrocen to alter joint pain and [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-02-28 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1002] => Array
(
[id] => 1002
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/identification-of-fam173b-as-a-protein-methyltransferase-promoting-chronic-pain-n1002
[title] => Identification of FAM173B as a protein methyltransferase promoting chronic pain
[paragraph_crop] => Identification of FAM173B as a protein methyltransferase promoting chronic pain
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-02-14 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[936] => Array
(
[id] => 936
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/oral-administration-of-undenatured-native-chicken-type-ii-collagen--uc-ii--diminished-deterioration-of-articular-cartilage-in-a-rat-model-of-osteoarthritis--oa--n936
[title] => Oral administration of undenatured native chicken type II collagen -UC-II- diminished deterioration of articular cartilage in a rat model of osteoarthritis -OA-
[paragraph_crop] => Oral administration of undenatured native chicken type II collagen (UC-II) diminished [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2017-12-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[969] => Array
(
[id] => 969
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/adjustment-of-the-dynamic-weight-distribution-as-a-sensitive-parameter-for-diagnosis-of-postural-alteration-in-a-rodent-model-of-vestibular-deficit-n969
[title] => Adjustment of the dynamic weight distribution as a sensitive parameter for diagnosis of postural alteration in a rodent model of vestibular deficit
[paragraph_crop] => Adjustment of the dynamic weight distribution as a sensitive parameter for diagnosis of [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2017-11-07 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[13] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 13
[title] => Système sensoriel
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-sensoriel
)
[49] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 49
[title] => Système vestibulaire
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-vestibulaire
)
)
)
[939] => Array
(
[id] => 939
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/optical-cuff-for-optogenetic-control-of-the-peripheral-nervous-system-n939
[title] => Optical cuff for optogenetic control of the peripheral nervous system
[paragraph_crop] => Optical cuff for optogenetic control of the peripheral nervous system
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2017-10-02 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[96] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 96
[title] => Autres pathologies
[link_rewrite] => Autres-pathologies
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[25] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 25
[title] => Thematiques diverses
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-diverses
)
)
)
[952] => Array
(
[id] => 952
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/effects-of-mollugo-pentaphylla-extract-on-monosodium-urate-crystal-induced-gouty-arthritis-in-mice-n952
[title] => Effects of Mollugo pentaphylla extract on monosodium urate crystal-induced gouty arthritis in mice
[paragraph_crop] => Effects of Mollugo pentaphylla extract on monosodium urate crystal-induced gouty arthritis in mice
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2017-09-06 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[912] => Array
(
[id] => 912
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/methods-used-to-evaluate-pain-behaviors-in-rodents-n912
[title] => Methods Used to Evaluate Pain Behaviors in Rodents
[paragraph_crop] => Methods Used to Evaluate Pain Behaviors in Rodents
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2017-09-06 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[34] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 34
[title] => Douleurs spontanées
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-spontanées
)
[87] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 87
[title] => Phénotypage
[link_rewrite] => Phenotypage
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[978] => Array
(
[id] => 978
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/thirty-five-day-fluoxetine-treatment-limits-sensory-motor-decit-and-biochemical-disorders-in-a-rat-model-of-decompression-sickness-n978
[title] => Thirty-five Day Fluoxetine Treatment Limits Sensory-Motor DeÞcit and Biochemical Disorders in a Rat Model of Decompression Sickness
[paragraph_crop] => Thirty-five Day Fluoxetine Treatment Limits Sensory-Motor DeÞcit and Biochemical Disorders in [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2017-09-05 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[23] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 23
[title] => Métabolisme
[link_rewrite] => Metabolisme
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[86] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 86
[title] => Stress oxydant
[link_rewrite] => Stress-oxydant
)
)
)
[934] => Array
(
[id] => 934
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/dynamic-weight-bearing-analysis-is-effective-for-evaluation-of-tendinopathy-using-a-customized-corridor-with-multi-directional-force-sensors-in-a-rat-model-n934
[title] => Dynamic weight bearing analysis is effective for evaluation of tendinopathy using a customized corridor with multi-directional force sensors in a rat model
[paragraph_crop] => Dynamic weight bearing analysis is effective for evaluation of tendinopathy using a customized [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2017-08-18 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[73] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 73
[title] => Ligaments
[link_rewrite] => Ligaments
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[907] => Array
(
[id] => 907
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/voluntary-and-evoked-behavioral-correlates-in-neuropathic-pain-states-under-different-social-housing-conditions-n907
[title] => Voluntary and evoked behavioral correlates in neuropathic pain states under different social housing conditions
[paragraph_crop] => Voluntary and evoked behavioral correlates in neuropathic pain states under different social [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2017-06-15 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[858] => Array
(
[id] => 858
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/biallelic-mutations-in-pde10a-lead-to-loss-of-striatal-pde10a-and-a-hyperkinetic-movement-disorder-with-onset-in-infancy-n858
[title] => Biallelic Mutations in PDE10A Lead to Loss of Striatal PDE10A and a Hyperkinetic Movement Disorder with Onset in Infancy
[paragraph_crop] => Biallelic Mutations in PDE10A Lead to Loss of Striatal PDE10A and a Hyperkinetic Movement [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2016-04-07 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[814] => Array
(
[id] => 814
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/proteinase-activated-receptor-2-modulates-oa-related-pain--cartilage-and-bone-pathology-n814
[title] => Proteinase-activated receptor 2 modulates OA-related pain- cartilage and bone pathology
[paragraph_crop] => Proteinase-activated receptor 2 modulates OA-related pain, cartilage and bone pathology
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-11-24 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[815] => Array
(
[id] => 815
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/dynamic-weight-bearing-is-an-efficient-and-predictable-method-for-evaluation-of-arthritic-nociception-and-its-pathophysiological-mechanisms-in-mice-n815
[title] => Dynamic weight bearing is an efficient and predictable method for evaluation of arthritic nociception and its pathophysiological mechanisms in mice
[paragraph_crop] => Dynamic weight bearing is an efficient and predictable method for evaluation of arthritic [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-10-29 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[740] => Array
(
[id] => 740
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/bone-metastasis-treatment-using-magnetic-resonance-guided-high-intensity-focused-ultrasound-n740
[title] => Bone Metastasis Treatment Using Magnetic Resonance-guided High Intensity Focused Ultrasound
[paragraph_crop] => Bone Metastasis Treatment Using Magnetic Resonance-guided High Intensity Focused Ultrasound
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-09-29 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[90] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 90
[title] => Cancer
[link_rewrite] => Cancer
)
[75] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 75
[title] => Fractures
[link_rewrite] => Fractures
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[22] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 22
[title] => Système squelettique
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-squelettique
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[742] => Array
(
[id] => 742
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/correlation-between-ct-imaging--histology-and-functional-capacity-of-the-osteoarthritic-knee-in-the-rat-model-of-osteoarthritis-n742
[title] => Correlation between ?CT imaging- histology and functional capacity of the osteoarthritic knee in the rat model of osteoarthritis
[paragraph_crop] => Correlation between ?CT imaging, histology and functional capacity of the osteoarthritic knee [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-08-25 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[752] => Array
(
[id] => 752
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/the-effects-of-endocannabinoid-modulation-and-neurogenic-inflammation-in-experimental-knee-joint-arthritis-n752
[title] => The Effects of Endocannabinoid Modulation and Neurogenic Inflammation in Experimental Knee Joint Arthritis
[paragraph_crop] => The Effects of Endocannabinoid Modulation and Neurogenic Inflammation in Experimental Knee [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-07-31 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[729] => Array
(
[id] => 729
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/reduction-of-neuropathic-and-inflammatory-pain-through-inhibition-of-the-tetrahydrobiopterin-pathway-n729
[title] => Reduction of Neuropathic and Inflammatory Pain through Inhibition of the Tetrahydrobiopterin Pathway
[paragraph_crop] => Reduction of Neuropathic and Inflammatory Pain through Inhibition of the Tetrahydrobiopterin Pathway
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-06-17 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[725] => Array
(
[id] => 725
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/a-multi-target-approach-for-pain-treatment--dual-inhibition-of-fatty-acid-amide-hydrolase-and-trpv1-in-a-rat-model-of-osteoarthritis-n725
[title] => A multi-target approach for pain treatment- dual inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase and TRPV1 in a rat model of osteoarthritis
[paragraph_crop] => A multi-target approach for pain treatment: dual inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase and [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-05-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[723] => Array
(
[id] => 723
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/evaluation-of-dynamic-weight-bearing-for-measuring-nonevoked-inflammatory-hyperalgesia-in-mice-n723
[title] => Evaluation of Dynamic Weight Bearing for Measuring Nonevoked Inflammatory Hyperalgesia in Mice
[paragraph_crop] => Evaluation of Dynamic Weight Bearing for Measuring Nonevoked Inflammatory Hyperalgesia in Mice
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-04-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[665] => Array
(
[id] => 665
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/orthopedic-surgery-and-bone-fracture-pain-are-both-significantly-attenuated-by-sustained-blockade-of-nerve-growth-factor-n665
[title] => Orthopedic surgery and bone fracture pain are both significantly attenuated by sustained blockade of nerve growth factor
[paragraph_crop] => Orthopedic surgery and bone fracture pain are both significantly attenuated by sustained [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-01-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[75] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 75
[title] => Fractures
[link_rewrite] => Fractures
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[22] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 22
[title] => Système squelettique
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-squelettique
)
)
)
[670] => Array
(
[id] => 670
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/polytherapy-with-a-combination-of-three-repurposed-drugs--pxt3003--down-regulates-pmp22-over-expression-and-improves-myelination--axonal-and-functional-parameters-in-models-of-cmt1a-neuropathy-n670
[title] => Polytherapy with a combination of three repurposed drugs -PXT3003- down-regulates Pmp22 over-expression and improves myelination- axonal and functional parameters in models of CMT1A neuropathy
[paragraph_crop] => Polytherapy with a combination of three repurposed drugs (PXT3003) down-regulates Pmp22 [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-12-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[67] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 67
[title] => Sclérose Latérale Amyotrophique (SLA), ou Maladie de Charcot
[link_rewrite] => Sclerose-Laterale-Amyotrophique-SLA-ou-Maladie-de-Charcot
)
[20] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 20
[title] => Système musculaire
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-musculaire
)
)
)
[699] => Array
(
[id] => 699
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/ngf-blockade-at-early-times-during-bone-cancer-development-attenuates-bone-destruction-and-increases-limb-use-n699
[title] => NGF blockade at early times during bone cancer development attenuates bone destruction and increases limb use
[paragraph_crop] => NGF blockade at early times during bone cancer development attenuates bone destruction and [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-12-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[90] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 90
[title] => Cancer
[link_rewrite] => Cancer
)
[75] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 75
[title] => Fractures
[link_rewrite] => Fractures
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[22] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 22
[title] => Système squelettique
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-squelettique
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[575] => Array
(
[id] => 575
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/use-of-dynamic-weight-bearing-as-a-novel-end-point-for-the-assessment-of-abdominal-pain-in-the-lps-induced-peritonitis-model-in-the-rat-n575
[title] => Use of dynamic weight bearing as a novel end-point for the assessment of abdominal pain in the LPS-induced peritonitis model in the rat
[paragraph_crop] => Use of dynamic weight bearing as a novel end-point for the assessment of abdominal pain in the [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-05-24 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[32] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 32
[title] => Douleurs abdominales, ovaro-pelviennes et liées à l'endométriose
[link_rewrite] => douleurs-abdominales-ovaro-pelviennes-et-liees-a-l-endometriose
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[98] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 98
[title] => Maladies auto-immunes
[link_rewrite] => Maladies-auto-immunes
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[577] => Array
(
[id] => 577
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/repair-of-the-injured-spinal-cord-by-implantation-of-a-synthetic-degradable-block-copolymer-in-rat-n577
[title] => Repair of the injured spinal cord by implantation of a synthetic degradable block copolymer in rat
[paragraph_crop] => Repair of the injured spinal cord by implantation of a synthetic degradable block copolymer in rat
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-05-10 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[39] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 39
[title] => Moelle épinière
[link_rewrite] => Moelle-epiniere
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[812] => Array
(
[id] => 812
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/pain-assessment-in-animal-models-of-osteoarthritis-n812
[title] => Pain assessment in animal models of osteoarthritis
[paragraph_crop] => Pain assessment in animal models of osteoarthritis
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-03-10 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[497] => Array
(
[id] => 497
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/a-new-method-to-assess-weight-bearing-distribution-after-central-nervous-system-lesions-in-rats-n497
[title] => A new method to assess weight-bearing distribution after central nervous system lesions in rats
[paragraph_crop] => A new method to assess weight-bearing distribution after central nervous system lesions in rats
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-11-04 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[816] => Array
(
[id] => 816
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/a-new-method-to-assess-weight-bearing-distribution-after-central-nervous-system-lesions-in-rats-n816
[title] => A new method to assess weight-bearing distribution after central nervous system lesions in rats
[paragraph_crop] => A new method to assess weight-bearing distribution after central nervous system lesions in rats
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-10-26 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[40] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 40
[title] => Accidents ischémiques transitoires (AIT)
[link_rewrite] => Accidents-ischemiques-transitoires-AIT
)
[39] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 39
[title] => Moelle épinière
[link_rewrite] => Moelle-epiniere
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[493] => Array
(
[id] => 493
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/spinal-nts2-receptor-activation-reverses-signs-of-neuropathic-pain--n493
[title] => Spinal NTS2 receptor activation reverses signs of neuropathic pain-
[paragraph_crop] => Spinal NTS2 receptor activation reverses signs of neuropathic pain.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-06-12 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[419] => Array
(
[id] => 419
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/comparison-of-evoked-and-non-evoked-endpoints-in-a-rodent-pain-model-and-potential-relevance-to-non-evoked-human-pain--n419
[title] => Comparison of evoked and non-evoked endpoints in a rodent pain model and potential relevance to non-evoked human pain-
[paragraph_crop] => Comparison of evoked and non-evoked endpoints in a rodent pain model and potential relevance [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2012-10-15 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[425] => Array
(
[id] => 425
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/a-micro-imaging-study-linking-bone-cancer-pain-with-tumor-growth-and-bone-resorption-in-a-rat-model-n425
[title] => A micro-imaging study linking bone cancer pain with tumor growth and bone resorption in a rat model
[paragraph_crop] => A micro-imaging study linking bone cancer pain with tumor growth and bone resorption in a rat model
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2012-09-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[90] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 90
[title] => Cancer
[link_rewrite] => Cancer
)
[75] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 75
[title] => Fractures
[link_rewrite] => Fractures
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[22] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 22
[title] => Système squelettique
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-squelettique
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[480] => Array
(
[id] => 480
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/use-of-dynamic-weight-bearing-as-a-novel-end-point-for-the-assessment-of-freunds-complete-adjuvant-induced-hypersensitivity-in-mice-n480
[title] => Use of dynamic weight bearing as a novel end-point for the assessment of Freund's Complete Adjuvant induced hypersensitivity in mice
[paragraph_crop] => Use of dynamic weight bearing as a novel end-point for the assessment of Freund's Complete [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2012-08-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[396] => Array
(
[id] => 396
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/inflammation-induced-decrease-in-voluntary-wheel-running-in-mice--a-nonreflexive-test-for-evaluating-inflammatory-pain-and-analgesia--n396
[title] => Inflammation-induced decrease in voluntary wheel running in mice- a nonreflexive test for evaluating inflammatory pain and analgesia-
[paragraph_crop] => Inflammation-induced decrease in voluntary wheel running in mice: a nonreflexive test for [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2012-04-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[375] => Array
(
[id] => 375
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/neuroplasticity-of-sensory-and-sympathetic-nerve-fibers-in-the-painful-arthritic-joint---n375
[title] => Neuroplasticity of sensory and sympathetic nerve fibers in the painful arthritic joint-
[paragraph_crop] => Neuroplasticity of sensory and sympathetic nerve fibers in the painful arthritic joint.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2012-01-13 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[417] => Array
(
[id] => 417
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/weight-bearing-evaluation-in-inflammatory--neuropathic-and-cancer-chronic-pain-in-freely-moving-rats-n417
[title] => Weight bearing evaluation in inflammatory- neuropathic and cancer chronic pain in freely moving rats
[paragraph_crop] => Weight bearing evaluation in inflammatory, neuropathic and cancer chronic pain in freely moving rats
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2011-09-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[90] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 90
[title] => Cancer
[link_rewrite] => Cancer
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[416] => Array
(
[id] => 416
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/nav1-9-channel-contributes-to-mechanical-and-heat-pain-hypersensitivity-induced-by-subacute-and-chronic-inflammation-n416
[title] => Nav1-9 Channel Contributes to Mechanical and Heat Pain Hypersensitivity Induced by Subacute and Chronic Inflammation
[paragraph_crop] => Nav1.9 Channel Contributes to Mechanical and Heat Pain Hypersensitivity Induced by Subacute [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2011-08-12 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[316] => Array
(
[id] => 316
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/acid-sensing-ion-channels-in-postoperative-pain---n316
[title] => Acid-Sensing Ion Channels in Postoperative Pain-
[paragraph_crop] => Acid-Sensing Ion Channels in Postoperative Pain.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2011-04-20 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[33] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 33
[title] => Douleurs post-opératoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-post-opératoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[283] => Array
(
[id] => 283
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/behavioral--medical-imaging-and-histopathological-features-of-a-new-rat-model-of-bone-cancer-pain---n283
[title] => Behavioral- Medical Imaging and Histopathological Features of a New Rat Model of Bone Cancer Pain-
[paragraph_crop] => Behavioral, Medical Imaging and Histopathological Features of a New Rat Model of Bone Cancer Pain.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2010-10-29 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[90] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 90
[title] => Cancer
[link_rewrite] => Cancer
)
[75] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 75
[title] => Fractures
[link_rewrite] => Fractures
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[22] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 22
[title] => Système squelettique
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-squelettique
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[278] => Array
(
[id] => 278
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/alteration-of-sensory-neurons-and-spinal-response-to-an-experimental-osteoarthritis-pain-model---n278
[title] => Alteration of sensory neurons and spinal response to an experimental osteoarthritis pain model-
[paragraph_crop] => Alteration of sensory neurons and spinal response to an experimental osteoarthritis pain model.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2010-10-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[276] => Array
(
[id] => 276
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/articular-mesenchymal-stem-cell--msc--and-effects-of-growth-differentiation-factor-5--gdf-5---n276
[title] => Articular Mesenchymal Stem Cell -MSC- and Effects of Growth Differentiation Factor-5 -GDF-5--
[paragraph_crop] => Articular Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) and Effects of Growth Differentiation Factor-5 (GDF-5).
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2010-09-20 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[165] => Array
(
[id] => 165
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/polyamine-deficient-diet-to-relieve-pain-hypersensitivity--n165
[title] => Polyamine deficient diet to relieve pain hypersensitivity-
[paragraph_crop] => Polyamine deficient diet to relieve pain hypersensitivity.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2008-06-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
)
1Nombre de publications:
Test non douloureux pour mesurer le niveau d'inconfort (incapacitance) de petits animaux comme les rats et les souris via...
Un instrument unique qui ne fournit pas seulement la mesure indépendante et automatisée du poids porté par chaque patte d'un...
Étendez votre analyse grâce à des calculs posturaux et locomoteurs avancés
Le système de Distribution...
check_circle
check_circle