
Les Kits contextuels pour T2CT ont été conçus pour enrichir les études de préférence de place...

Les Kits contextuels pour T2CT ont été conçus pour enrichir les études de préférence de place...

Une méthode simple pour quantifier objectivement la force musculaire des rats et souris et...

La roue d'activité spontanée BIOSEB offre une solution efficace pour quantifier l'activité...

La Roue Instrumentée pour Exercice Spontané est une méthode simple pour mesurer l'activité...

Une façon simple pour mesurer l'activité des rongeurs sur plusieurs jours dans leurs cages de...

Conçu pour les études sur l'entraînement physique et la fatigue chez les rongeurs - et désormais...

Instrument de test de la sensibilité de l'animal à la douleur résultant de l'exposition à la...

Un test indépendant de l'opérateur pour étudier les seuils de douleur chez les rongeurs (rats et...

Le Test de Gradient Thermique indépendant de l'opérateur est un nouvel instrument de recherche...

Les Kits contextuels pour T2CT ont été conçus pour enrichir les études de préférence de place...

Un système permettant l'analyse de la posture des animaux par la répartition du poids sur...

Test non douloureux pour mesurer le niveau d'inconfort (incapacitance) de petits animaux comme...

Un instrument unique qui ne fournit pas seulement la mesure indépendante et automatisée du poids...
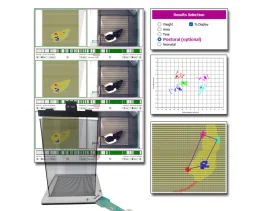
Étendez votre analyse grâce à des calculs posturaux et locomoteurs avancés Le système de...

Une solution rapide pour déterminer le seuil de sensibilité à la douleur mécanique chez les...

En tant que version électronique du classique esthésiomètre à filaments de Von Frey, la...

Nouvelles cage de contention modulables ROBUSTES pour maintenir doucement les rongeurs (rats et...

Une solution économique et versatile pour les situations nécessitant des tests sensoriels...

Dédié aux petits animaux tels que les rats et les souris, le Smalgo est un algomètre (ou...

La version 5 du Test de Suspension Caudale de Bioseb, basée sur des capteurs de force ainsi que...

NOUVEAU ! Solution complète (matériel et logiciel), dédiée et automatisée pour le Labyrinthe...

Un nouveau système innovant pour l'automatisation du test d'Open Field pour rats et souris:...

Test open-field - ARENE UNIQUEMENT utilisé pour évaluer l'activité basale des rongeurs (rats et...

Le nouveau Test de Nage Forcée Bioseb DUAL SENSOR à été développé selon une double approche: En...

Un nouveau système innovant pour l'automatisation du test de Reconnaissance d'Object ("Novel...

Test open-field - ARENE UNIQUEMENT utilisé pour évaluer l'activité basale des rongeurs (rats et...

Un système expérimental d'enclos entièrement modulable conçu pour conduire des procédures de...

Appareil d'utilisation très simple pour souris Possibilité de sortir les données sur PC

Une chambre expérimentale standard pour l'évaluation automatisée ou manuelle de la préférence de...
Mesures des paramètres physiologique en temps réel chez le rats - non invasive et sans aucune...

L'ETH-401 est un amplificateur de pont pour différents transducteurs qui fournit quatre canaux...

Le IX-118 est un système d'acquisition de données rapide 100 kHz à haute résolution et approprié...

L'ETH-256 est un amplificateur 2 canaux haute performance à usage général de la recherche en...

Stimulateur à canaux multiples toutes options pour stimulation neuro-musculaire

Découvrez BIO-FOODIS, la solution de nouvelle génération pour comprendre le comportement...

Système modulaire permettant l'intégration du métabolisme respiratoire, de l'apport de...

Équipements innovants et appropriés pour mesurer la consommation de nourriture / boisson ainsi...

Un analyseur d'oxygène et de dioxyde de carbone économique, de haute performance avec des taux...
Une solution rapide pour déterminer le seuil de sensibilité à la douleur mécanique chez les rongeurs (rats et souris). Maintenant en version sans-fil, pour être libéré des câbles!
Cet instrument électronique précis et simple d'utilisation est le test de référence pour vos recherches en analgésie, nociception, neuropathies et douleurs post-opératoires
![]()
![]()
![]() Présentation
Présentation
Les 16 années d’expérience de BIOSEB en instrumentation pour le test de Von Frey nous permettent de vous proposer un standard dans la mesure des seuils de sensibilité à la douleur mécanique chez les rongeurs (rats et souris).
Etudié pour améliorer la qualité des résultats et faciliter la prise de mesure comparés aux filaments de Von Frey qui demandent de nombreuses sollicitations pour chaque valeur et introduisent un stress chez l’animal, le test de Von Frey Electronique permet d’obtenir le seuil de sensibilité mécanique en une seule mesure.
Cette valeur, mesurée avec une résolution de 0.1 grammes grâce à un capteur de précision, permet de réduire le temps d’expérimentation et offre une meilleure répétabilité entre les différentes séries. Les résultats sont affichés sur un large écran rétro-éclairé. L'instrument électronique présente aussi l’avantage de n’avoir aucune dérive lié à la température ou à l’hygrométrie.
La plage étendue du capteur de mesure permet de travailler avec un grand nombre d’espèces (Rats, Souris, Homme…) avec le même instrument.
La dernière version du Von Frey Electronique intègre une nouvelle poignée de mesure intégralement repensée. Elle est plus facile à prendre en main mais aussi plus équilibrée de façon à simplifier la stimulation. Le confort d’utilisation réduit la fatigue de l’opérateur et diminue les tensions liées aux longues sessions de mesure sur un grand nombre d’animaux.La poignée intègre un nouveau capteur, plus précis et plus rigide, donc moins sensible au mouvements de l’opérateur. ![]() Principes de fonctionnement
Principes de fonctionnement
L’Instrument de Von Frey Electronique est composé d’une unité d’affichage électronique ainsi que d’une poignée de stimulation. Une pédale est aussi livrée pour la remise à 0 de la mesure. Une boite de 10 pointes en plastique interchangeables est fournie.
L’expérimentateur prend en main la poignée de l’appareil et stimule avec la pointe dédiée la zone d’intérêt.
• Stimulation sous la patte du rongeur :
La stimulation est généralement effectuée sur les patte arrières du rongeur. Le retrait de la patte causé par la stimulation mécanique est enregistré comme la réponse à ce stimulus. La force maximale appliquée avec l’appareil, correspondant à la valeur nécessaire pour le retrait de la patte, est sauvegardée par le système et affichée sur l’écran de l'unité électronique du Von Frey, avec une résolution de 0.1 gramme. Une pointe différente est utilisée pour le rat (pointe en plastique dur) et pour la souris (pointe souple).
• Utilisation spécifique pour l’utilisation chez le patient :
L’appareil, dans sa version dédiée à une usage chez l’Humain, est livré avec un bouton dit 'bouton patient', permettant au patient recevant la stimulation de figer lui-même la mesure sur l’écran de l’instrument lorsque le seuil désiré (sensibilité, douleur) est atteint.
![]() NOUVEAU: Sans fil
NOUVEAU: Sans fil
Une gamme complète d'instruments Bioseb, incluant le Von Frey Électronique, comprend désormais notre nouvelle technologie sans fil: grâce au boîtier sans fi placé sur le poignet de l'opérateur, il n'y a plus de câble entre la console éléctronique de l'écran et les capteurs
Cette nouvelle technologie sans fil offre de nombreux avantages:
• Mailleure liberté de mouvement: plus de câbes agaçants !
• Une configuration flexible pour votre laboratoire : concevez votre espace de travail sans limites
• Libérez vous des contraintes physiques : concentrez vous sur votre expérience !
![]() Options facilitant la tâche de l'opérateur
Options facilitant la tâche de l'opérateur
• 'Bouton - patient' permet de figer la valeur du seuil (lors d'expérimentation clinique )
• Liaison RS232 permet de transférer la valeur affichée sur un ordinateur
• Tablette tactile pour affichage vidéo
• Logiciel BIO-CIS2 (pour PC sous Windows 7 ou supérieur) permet de collecter directement ces valeurs sous EXCEL pour faciliter leur analyse
![]() Livré avec
Livré avec
• 1 Mallette
• Une pédale à pied pour la mise à zéro au démarrage du test en gardant les 2 mains libres
• 10 pointes de mesure jetables de 0,5 mm de diamètre
• Une pointe ressort pour seuils de 0-10 grammes
• En option : le « bouton patient » pour un usage chez l’Homme. Cliquez ici pour en savoir plus!![]() Nouveau système AlgoKit
Nouveau système AlgoKit
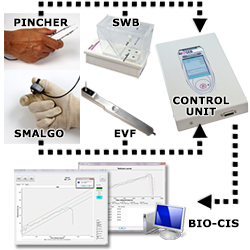
Vous pouvez également être intéressé par notre nouveau système ALGOKIT afin d'étendre le champs des possibles pour vos recherches. Pour répondre aux diverses demandes concernant les différents cas possibles en mesure de la douleur et pour faire face à toutes les situations, Bioseb est fière de présenter l'AlgoKit construit autour de notre test d'Incapacitance Statique (SWB: Distribution Pondérale Statique), avec son écran tactile couleurs, et de jusqu'à 3 capteurs additionnels parmi notreVon Frey Électronique, de la Pince Instrumentée et de l'algomètre pour petits animaux (SMALGO) combinés à un unique boitier de contrôle ! .
Avantages:
• Flexibilité : solution complète pour les mesure d’analgésie à portée de main !
• Compatible avec le logiciel d'acquisition BIO-CIS2 pour améliorer la répétabilité des tests nociceptifs.
Fiche technique
Array
(
[2029] => Array
(
[id] => 2029
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Exosomes-derived-from-platelet-rich-plasma-alleviate-synovial-inflammation-by-enhancing-synovial-lymphatic-function-n2029
[title] => Exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma alleviate synovial inflammation by enhancing synovial lymphatic function
[paragraph_crop] => Exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma alleviate synovial inflammation by enhancing [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-12-19 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[96] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 96
[title] => Autres pathologies
[link_rewrite] => Autres-pathologies
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2142] => Array
(
[id] => 2142
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Evaluating-the-usage-of-human-placental-tissue-derived-xenograft-in-a-surgically-induced-murine-fracture-model-n2142
[title] => Evaluating the usage of human placental tissue-derived xenograft in a surgically induced murine fracture model
[paragraph_crop] => Evaluating the usage of human placental tissue-derived xenograft in a surgically induced [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-11-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[75] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 75
[title] => Fractures
[link_rewrite] => Fractures
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2147] => Array
(
[id] => 2147
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Spinal-p38-MAPK-and-PGC-1alpha-and-SIRT3-signaling-pathway-mediates-remifentanil-induced-hyperalgesia-in-rats-via-ROS-release-and-NR2B-activation-n2147
[title] => Spinal p38 MAPK and PGC-1alpha and SIRT3 signaling pathway mediates remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia in rats via ROS release and NR2B activation
[paragraph_crop] => Spinal p38 MAPK and PGC-1alpha and SIRT3 signaling pathway mediates remifentanil-induced [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-11-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2025] => Array
(
[id] => 2025
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Neuronutritional-enhancement-of-antioxidant-defense-system-through-Nrf2-and-HO1-and-NQO1-axis-in-fibromyalgia-n2025
[title] => Neuronutritional enhancement of antioxidant defense system through Nrf2 and HO1 and NQO1 axis in fibromyalgia
[paragraph_crop] => Neuronutritional enhancement of antioxidant defense system through Nrf2 and HO1 and NQO1 axis [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-11-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2022] => Array
(
[id] => 2022
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Evaluation-of-peripheral-analgesia-in-a-rat-incisional-pain-model-using-degradable-hydrophilic-microspheres-for-sustained-delivery-of-buprenorphine-n2022
[title] => Evaluation of peripheral analgesia in a rat incisional pain model using degradable hydrophilic microspheres for sustained delivery of buprenorphine
[paragraph_crop] => Evaluation of peripheral analgesia in a rat incisional pain model using degradable hydrophilic [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-09-02 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2113] => Array
(
[id] => 2113
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Ablation-of-VEGFA-following-a-lumbar-intervertebral-disc-injury-attenuates-intradiscal-neurovascular-features-and-prevents-chronic-low-back-pain-symptoms-n2113
[title] => Ablation of VEGFA following a lumbar intervertebral disc injury attenuates intradiscal neurovascular features and prevents chronic low back pain symptoms
[paragraph_crop] => Ablation of VEGFA following a lumbar intervertebral disc injury attenuates intradiscal [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-09-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2023] => Array
(
[id] => 2023
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Comorbid-hypertension-and-osteoarthritis-exacerbates-joint-remodeling-and-gait-compensations-in-female-rats-with-milder-effects-observed-in-males-n2023
[title] => Comorbid hypertension and osteoarthritis exacerbates joint remodeling and gait compensations in female rats with milder effects observed in males
[paragraph_crop] => Comorbid hypertension and osteoarthritis exacerbates joint remodeling and gait compensations [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-09-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2020] => Array
(
[id] => 2020
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/The-Synergistic-Effect-of-Heat-Therapy-and-Electroacupuncture-Treatment-in-Inflammatory-Pain-Mouse-Models-n2020
[title] => The Synergistic Effect of Heat Therapy and Electroacupuncture Treatment in Inflammatory Pain Mouse Models
[paragraph_crop] => The Synergistic Effect of Heat Therapy and Electroacupuncture Treatment in Inflammatory Pain [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-08-19 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[96] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 96
[title] => Autres pathologies
[link_rewrite] => Autres-pathologies
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2028] => Array
(
[id] => 2028
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Characterization-of-a-mouse-model-of-osteoarticular-infection-using-clinical-isolates-of-Staphylococcus-aureus-n2028
[title] => Characterization of a mouse model of osteoarticular infection using clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus
[paragraph_crop] => Characterization of a mouse model of osteoarticular infection using clinical isolates of [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-08-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2027] => Array
(
[id] => 2027
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Assessment-of-Postoperative-Analgesic-Efficacy-and-Animal-Well-Being-Using-a-Novel-Triaxial-Accelerometer-Device--the-Rodent-Fitbit-Like-Telemetry-Device-n2027
[title] => Assessment of Postoperative Analgesic Efficacy and Animal Well-Being Using a Novel Triaxial Accelerometer Device- the Rodent Fitbit-Like Telemetry Device
[paragraph_crop] => Assessment of Postoperative Analgesic Efficacy and Animal Well-Being Using a Novel Triaxial [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-05-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[96] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 96
[title] => Autres pathologies
[link_rewrite] => Autres-pathologies
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2017] => Array
(
[id] => 2017
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Inhibition-of-SARM1-Reduces-Neuropathic-Pain-in-a-Spared-Nerve-Injury-Rodent-Model-n2017
[title] => Inhibition of SARM1 Reduces Neuropathic Pain in a Spared Nerve Injury Rodent Model
[paragraph_crop] => Inhibition of SARM1 Reduces Neuropathic Pain in a Spared Nerve Injury Rodent Model
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-04-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2018] => Array
(
[id] => 2018
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/ART26-12--a-novel-fatty-acid-binding-protein-5-inhibitor--shows-efficacy-in-multiple-preclinical-neuropathy-models-n2018
[title] => ART26-12- a novel fatty acid-binding protein 5 inhibitor- shows efficacy in multiple preclinical neuropathy models
[paragraph_crop] => ART26-12- a novel fatty acid-binding protein 5 inhibitor- shows efficacy in multiple [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-02-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2021] => Array
(
[id] => 2021
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Ageing-Related-Macrophage-Polarisation-in-the-Trigeminal-Ganglion-Enhances-Incisional-Intraoral-Pain-n2021
[title] => Ageing-Related Macrophage Polarisation in the Trigeminal Ganglion Enhances Incisional Intraoral Pain
[paragraph_crop] => Ageing-Related Macrophage Polarisation in the Trigeminal Ganglion Enhances Incisional Intraoral Pain
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-02-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2007] => Array
(
[id] => 2007
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Nano-fiber-and-net-artificial-bionic-dura-mater-promotes-neural-stem-cell-differentiating-by-time-sequence-external-oral-administration-to-repair-spinal-cord-injury-n2007
[title] => Nano-fiber and net artificial bionic dura mater promotes neural stem cell differentiating by time sequence external-oral administration to repair spinal cord injury
[paragraph_crop] => Nano-fiber and net artificial bionic dura mater promotes neural stem cell differentiating by [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-01-27 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[39] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 39
[title] => Moelle épinière
[link_rewrite] => Moelle-epiniere
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2026] => Array
(
[id] => 2026
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Interplay-between-subthalamic-nucleus-and-spinal-cord-controls-parkinsonian-nociceptive-disorders-n2026
[title] => Interplay between subthalamic nucleus and spinal cord controls parkinsonian nociceptive disorders
[paragraph_crop] => Interplay between subthalamic nucleus and spinal cord controls parkinsonian nociceptive disorders
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-01-07 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2019] => Array
(
[id] => 2019
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Developing-a-model-of-temporomandibular-disorder-in-the-common-marmoset-using-nerve-growth-factor-n2019
[title] => Developing a model of temporomandibular disorder in the common marmoset using nerve growth factor
[paragraph_crop] => Developing a model of temporomandibular disorder in the common marmoset using nerve growth factor
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-01-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[79] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 79
[title] => Adiposité
[link_rewrite] => Adiposite
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[2024] => Array
(
[id] => 2024
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/Targeting-IL-20-alleviates-inflammatory-mechanical-allodynia-and-reduces-epidural-fibrosis-in-post-laminectomy-syndrome-rat-model-n2024
[title] => Targeting IL-20 alleviates inflammatory mechanical allodynia and reduces epidural fibrosis in post-laminectomy syndrome rat model
[paragraph_crop] => Targeting IL-20 alleviates inflammatory mechanical allodynia and reduces epidural fibrosis in [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2025-01-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[96] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 96
[title] => Autres pathologies
[link_rewrite] => Autres-pathologies
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1967] => Array
(
[id] => 1967
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/interplay-between-subthalamic-nucleus-and-spinal-cord-controls-parkinsonian-nociceptive-disorders-n1967
[title] => Interplay between subthalamic nucleus and spinal cord controls parkinsonian nociceptive disorders
[paragraph_crop] => Interplay between subthalamic nucleus and spinal cord controls parkinsonian nociceptive disorders
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2024-06-25 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1960] => Array
(
[id] => 1960
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/sorafenib-inhibits-ossification-of-the-posterior-longitudinal-ligament-by-blocking-loxl2-mediated-vascularization-n1960
[title] => Sorafenib inhibits ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament by blocking LOXL2-mediated vascularization
[paragraph_crop] => Sorafenib inhibits ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament by blocking [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2024-04-10 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[39] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 39
[title] => Moelle épinière
[link_rewrite] => Moelle-epiniere
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1958] => Array
(
[id] => 1958
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/link-protein-1-is-involved-in-the-activity-dependent-modulation-of-perineuronal-nets-in-the-spinal-cord-n1958
[title] => Link Protein 1 Is Involved in the Activity-Dependent Modulation of Perineuronal Nets in the Spinal Cord
[paragraph_crop] => Link Protein 1 Is Involved in the Activity-Dependent Modulation of Perineuronal Nets in the [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2024-03-20 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[39] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 39
[title] => Moelle épinière
[link_rewrite] => Moelle-epiniere
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1939] => Array
(
[id] => 1939
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/purine-nucleoside-phosphorylase-inhibition-is-an-effective-approach-for-the-treatment-of-chemical-hemorrhagic-cystitis-n1939
[title] => Purine nucleoside phosphorylase inhibition is an effective approach for the treatment of chemical hemorrhagic cystitis
[paragraph_crop] => Purine nucleoside phosphorylase inhibition is an effective approach for the treatment of [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2024-03-08 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1946] => Array
(
[id] => 1946
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/beneficial-effects-of-photoperiod-lengthening-on-sleep-characteristics-and-mechanical-hyperalgesia-in-injured-rats-n1946
[title] => Beneficial effects of photoperiod lengthening on sleep characteristics and mechanical hyperalgesia in injured rats
[paragraph_crop] => Beneficial effects of photoperiod lengthening on sleep characteristics and mechanical [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2024-03-07 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1951] => Array
(
[id] => 1951
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/nanoporous-graphene-based-thin-film-microelectrodes-for-in-vivo-high-resolution-neural-recording-and-stimulation-n1951
[title] => Nanoporous graphene-based thin-film microelectrodes for in vivo high-resolution neural recording and stimulation
[paragraph_crop] => Nanoporous graphene-based thin-film microelectrodes for in vivo high-resolution neural [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2024-01-11 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[37] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 37
[title] => Fonctions cérébrales
[link_rewrite] => Fonctions-cerebrales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1954] => Array
(
[id] => 1954
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/creb1-facilitates-gabaergic-neural-differentiation-of-human-mesenchymal-stem-cells-through-brn2-for-pain-alleviation-and-locomotion-recovery-after-spinal-cord-injury-n1954
[title] => CREB1 Facilitates GABAergic Neural Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells through BRN2 for Pain Alleviation and Locomotion Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury
[paragraph_crop] => CREB1 Facilitates GABAergic Neural Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells through [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2023-12-28 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1912] => Array
(
[id] => 1912
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/exploring-serum-biomarkers-for-neuropathic-pain-in-rat-models-of-chemotherapy-induced-peripheral-neuropathy--a-comparative-pilot-study-with-oxaliplatin--paclitaxel--bortezomib--and-vincristine-n1912
[title] => Exploring Serum Biomarkers for Neuropathic Pain in Rat Models of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy- A Comparative Pilot Study with Oxaliplatin- Paclitaxel- Bortezomib- and Vincristine
[paragraph_crop] => Exploring Serum Biomarkers for Neuropathic Pain in Rat Models of Chemotherapy-Induced [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2023-12-08 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1852] => Array
(
[id] => 1852
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/description-of-novel-molecular-factors-in-lumbar-drgs-and-spinal-cord-factors-underlying-development-of-neuropathic-pain-component-in-the-animal-model-of-osteoarthritis-n1852
[title] => Description of Novel Molecular Factors in Lumbar DRGs and Spinal Cord Factors Underlying Development of Neuropathic Pain Component in the Animal Model of Osteoarthritis
[paragraph_crop] => Description of Novel Molecular Factors in Lumbar DRGs and Spinal Cord Factors Underlying [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2023-09-21 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1870] => Array
(
[id] => 1870
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/dual-piperidine-based-histamine-h3-and-sigma-1-receptor-ligands-in-the-treatment-of-nociceptive-and-neuropathic-pain-n1870
[title] => Dual Piperidine-Based Histamine H3 and Sigma-1 Receptor Ligands in the Treatment of Nociceptive and Neuropathic Pain
[paragraph_crop] => Dual Piperidine-Based Histamine H3 and Sigma-1 Receptor Ligands in the Treatment of [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2023-07-07 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1882] => Array
(
[id] => 1882
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/descending-serotonergic-modulation-from-rostral-ventromedial-medulla-to-spinal-trigeminal-nucleus-is-involved-in-experimental-occlusal-interference-induced-chronic-orofacial-hyperalgesia-n1882
[title] => Descending serotonergic modulation from rostral ventromedial medulla to spinal trigeminal nucleus is involved in experimental occlusal interference-induced chronic orofacial hyperalgesia
[paragraph_crop] => Descending serotonergic modulation from rostral ventromedial medulla to spinal trigeminal [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2023-05-10 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[31] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 31
[title] => Douleurs oro-faciales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-oro-faciales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1860] => Array
(
[id] => 1860
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/injectable-hypoxia-preconditioned-cartilage-progenitor-cells-laden-gelma-microspheres-system-for-enhanced-osteoarthritis-treatment-n1860
[title] => Injectable hypoxia-preconditioned cartilage progenitor cells-laden GelMA microspheres system for enhanced osteoarthritis treatment
[paragraph_crop] => Injectable hypoxia-preconditioned cartilage progenitor cells-laden GelMA microspheres system [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2023-04-17 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1885] => Array
(
[id] => 1885
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/minimally-invasive-periarticular-injections-of-local-anesthetic-provides-prolonged-analgesia-in-a-rodent-osteoarthritis-model-n1885
[title] => Minimally Invasive Periarticular Injections Of Local Anesthetic Provides Prolonged Analgesia In A Rodent Osteoarthritis Model
[paragraph_crop] => Minimally Invasive Periarticular Injections Of Local Anesthetic Provides Prolonged Analgesia [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2023-04-04 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1841] => Array
(
[id] => 1841
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/shenqisherong-pill-ameliorates-neuronal-apoptosis-by-inhibiting-the-jnk-and-caspase-3-signaling-pathway-in-a-rat-model-of-cervical-cord-compres-n1841
[title] => Shenqisherong pill ameliorates neuronal apoptosis by inhibiting the JNK and caspase-3 signaling pathway in a rat model of cervical cord compres
[paragraph_crop] => Shenqisherong pill ameliorates neuronal apoptosis by inhibiting the JNK and caspase-3 [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2023-01-10 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[63] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 63
[title] => Système musculaire général
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-musculaire-general
)
)
)
[1539] => Array
(
[id] => 1539
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/enhanced-pain-facilitation-rather-than-impaired-pain-inhibition-in-burning-mouth-syndrome-female-patients-n1539
[title] => Enhanced pain facilitation rather than impaired pain inhibition in burning mouth syndrome female patients
[paragraph_crop] => Enhanced pain facilitation rather than impaired pain inhibition in burning mouth syndrome [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-08-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1543] => Array
(
[id] => 1543
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/targeting-trpv1-activity-via-highdose-capsaicin-in-patients-with-sickle-cell-disease-n1543
[title] => Targeting TRPV1 activity via high‐dose capsaicin in patients with sickle cell disease
[paragraph_crop] => Targeting TRPV1 activity via high‐dose capsaicin in patients with sickle cell disease
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-06-27 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[96] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 96
[title] => Autres pathologies
[link_rewrite] => Autres-pathologies
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1547] => Array
(
[id] => 1547
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/rvd1-disrupts-nociceptor-neuron-and-macrophage-activation-and-neuroimmune-communication--reducing-pain-and-inflammation-in-gouty-arthritis-in-mice-n1547
[title] => RvD1 disrupts nociceptor neuron and macrophage activation and neuroimmune communication- reducing pain and inflammation in gouty arthritis in mice
[paragraph_crop] => RvD1 disrupts nociceptor neuron and macrophage activation and neuroimmune communication- [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-06-18 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1549] => Array
(
[id] => 1549
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/sciatic-nerve-stimulation-alleviates-acute-neuropathic-pain-via-modulation-of-neuroinflammation-and-descending-pain-inhibition-in-a-rodent-model-n1549
[title] => Sciatic nerve stimulation alleviates acute neuropathic pain via modulation of neuroinflammation and descending pain inhibition in a rodent model
[paragraph_crop] => Sciatic nerve stimulation alleviates acute neuropathic pain via modulation of [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-06-15 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1556] => Array
(
[id] => 1556
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/the-overexpression-of-insulin-like-growth-factor-1-and-neurotrophin-3-promote-functional-recovery-and-alleviate-spasticity-after-spinal-cord-injury-n1556
[title] => The Overexpression of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 and Neurotrophin-3 Promote Functional Recovery and Alleviate Spasticity After Spinal Cord Injury
[paragraph_crop] => The Overexpression of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 and Neurotrophin-3 Promote Functional [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-04-29 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[39] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 39
[title] => Moelle épinière
[link_rewrite] => Moelle-epiniere
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1527] => Array
(
[id] => 1527
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/early-life-pain-experience-changes-adult-functional-pain-connectivity-in-the-rat-somatosensory-and-the-medial-prefrontal-cortex-n1527
[title] => Early life pain experience changes adult functional pain connectivity in the rat somatosensory and the medial prefrontal cortex
[paragraph_crop] => Early life pain experience changes adult functional pain connectivity in the rat somatosensory [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-03-04 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[92] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 92
[title] => Petite enfance
[link_rewrite] => Petite-enfance
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1505] => Array
(
[id] => 1505
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/painful-diabetic-neuropathy-is-associated-with-compromised-microglial-igf-1-signaling-which-can-be-rescued-by-green-tea-polyphenol-egcg-in-mice-n1505
[title] => Painful Diabetic Neuropathy Is Associated with Compromised Microglial IGF-1 Signaling Which Can Be Rescued by Green Tea Polyphenol EGCG in Mice
[paragraph_crop] => Painful Diabetic Neuropathy Is Associated with Compromised Microglial IGF-1 Signaling Which [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-02-22 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[81] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 81
[title] => Diabète, Insuline & Glucose
[link_rewrite] => Diabète-Insuline-Glucose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1521] => Array
(
[id] => 1521
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/the-therapeutic-effect-of-imsc-derived-small-extracellular-vesicles-on-tendinopathy-related-pain-through-alleviating-inflammation--an-in-vivo-and-in-vitro-study-n1521
[title] => The Therapeutic Effect of iMSC-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles on Tendinopathy Related Pain Through Alleviating Inflammation- An in vivo and in vitro Study
[paragraph_crop] => The Therapeutic Effect of iMSC-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles on Tendinopathy Related [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-02-15 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[69] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 69
[title] => Recherche générale sur les articulations
[link_rewrite] => Recherche-generale-sur-les-articulations
)
)
)
[1502] => Array
(
[id] => 1502
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/probdnfp75ntr-promotes-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-inflammatory-response-by-activating-proinflammatory-cytokines-n1502
[title] => proBDNF/p75NTR promotes rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory response by activating proinflammatory cytokines
[paragraph_crop] => proBDNF/p75NTR promotes rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory response by activating proinflammatory
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-01-05 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1484] => Array
(
[id] => 1484
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/alpha-conotoxin-rgia-and-oligoarginine-r8-in-the-mice-model-alleviate-long-term-oxaliplatin-induced-neuropathy-n1484
[title] => Alpha-Conotoxin RgIA and oligoarginine R8 in the mice model alleviate long-term oxaliplatin induced neuropathy
[paragraph_crop] => Alpha-Conotoxin RgIA and oligoarginine R8 in the mice model alleviate long-term oxaliplatin [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2022-01-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[90] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 90
[title] => Cancer
[link_rewrite] => Cancer
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1483] => Array
(
[id] => 1483
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/small-extracellular-vesicles-derived-from-human-ipsc-derived-msc-ameliorate-tendinopathy-related-acute-pain-through-inhibiting-mast-cells-activation-n1483
[title] => Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Human Ipsc-Derived MSC Ameliorate Tendinopathy-Related Acute Pain Through Inhibiting Mast Cells Activation
[paragraph_crop] => Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Human Ipsc-Derived MSC Ameliorate [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-12-06 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1496] => Array
(
[id] => 1496
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/involvement-of-the-bdnftrkbkcc2-pathway-in-neuropathic-pain-after-brachial-plexus-avulsion-n1496
[title] => Involvement of the BDNFÐTrkBÐKCC2 pathway in neuropathic pain after brachial plexus avulsion
[paragraph_crop] => Involvement of the BDNFÐTrkBÐKCC2 pathway in neuropathic pain after brachial plexus avulsion
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-11-21 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1479] => Array
(
[id] => 1479
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/wntbeta-catenin-pathway-in-experimental-model-of-fibromyalgia-role-of-hidrox-n1479
[title] => Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway in Experimental Model of Fibromyalgia: Role of Hidrox
[paragraph_crop] => Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway in Experimental Model of Fibromyalgia: Role of Hidrox
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-11-13 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1443] => Array
(
[id] => 1443
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/contribution-of-trem2-signaling-to-the-development-of-painful-diabetic-neuropathy-by-mediating-microglial-polarization-in-mice-n1443
[title] => Contribution of Trem2 Signaling to the Development of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy by Mediating Microglial Polarization in Mice
[paragraph_crop] => Contribution of Trem2 Signaling to the Development of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy by Mediating [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-10-26 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[81] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 81
[title] => Diabète, Insuline & Glucose
[link_rewrite] => Diabète-Insuline-Glucose
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1478] => Array
(
[id] => 1478
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/reversing-the-surface-charge-of-msc-derived-small-extracellular-vesicles-by-epsilonpl-peg-dspe-for-enhanced-osteoarthritis-treatment--n1478
[title] => Reversing the surface charge of MSC-derived small extracellular vesicles by epsilonPL-PEG-DSPE for enhanced osteoarthritis treatment
[paragraph_crop] => Reversing the surface charge of MSC-derived small extracellular vesicles by epsilonPL-PEG-DSPE [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-10-04 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1427] => Array
(
[id] => 1427
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/phenotypic-characterization-of-the-endocannabinoid-degrading-enzyme-alpha-and-beta-hydrolase-domain-6-knockout-rat-n1427
[title] => Phenotypic Characterization of the Endocannabinoid-Degrading Enzyme Alpha and Beta-Hydrolase Domain 6 Knockout Rat
[paragraph_crop] => Phenotypic Characterization of the Endocannabinoid-Degrading Enzyme Alpha and Beta-Hydrolase [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-08-31 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1456] => Array
(
[id] => 1456
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/behavioral-phenotyping-of-cancer-pain-in-domesticated-cats-with-naturally-occurring-squamous-cell-carcinoma-of-the-tongue--initial-validation-studies-provide-evidence-for-regional-and-widespread-algoplasticity-n1456
[title] => Behavioral phenotyping of cancer pain in domesticated cats with naturally occurring squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue- initial validation studies provide evidence for regional and widespread algoplasticity
[paragraph_crop] => Behavioral phenotyping of cancer pain in domesticated cats with naturally occurring squamous [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-08-16 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[97] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 97
[title] => Autres animaux
[link_rewrite] => Autres-animaux
)
[90] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 90
[title] => Cancer
[link_rewrite] => Cancer
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1451] => Array
(
[id] => 1451
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/novel-functionalized-amino-acids-as-inhibitors-of-gaba-transporters-with-analgesic-activity-n1451
[title] => Novel Functionalized Amino Acids as Inhibitors of GABA Transporters with Analgesic Activity
[paragraph_crop] => Novel Functionalized Amino Acids as Inhibitors of GABA Transporters with Analgesic Activity
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-08-04 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1424] => Array
(
[id] => 1424
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/modulatory-effect-of-probiotic-lactobacillus-rhamnosus-pb01-on-mechanical-sensitivity-in-a-female-diet-induced-obesity-model-n1424
[title] => Modulatory Effect of Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus PB01 on Mechanical Sensitivity in a Female Diet-Induced Obesity Model
[paragraph_crop] => Modulatory Effect of Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus PB01 on Mechanical Sensitivity in a [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-06-29 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[80] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 80
[title] => Obésité & Surpoids
[link_rewrite] => Obesite-Surpoids
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1422] => Array
(
[id] => 1422
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/genistein-reverses-the-effect-of-17betaestradiol-on-exacerbating-experimental-occlusal-interferenceinduced-chronic-masseter-hyperalgesia-in-ovariectomized-rats-n1422
[title] => Genistein reverses the effect of 17beta_estradiol on exacerbating experimental occlusal interference_induced chronic masseter hyperalgesia in ovariectomized rats
[paragraph_crop] => Genistein reverses the effect of 17beta_estradiol on exacerbating experimental occlusal [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-06-02 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[31] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 31
[title] => Douleurs oro-faciales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-oro-faciales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1414] => Array
(
[id] => 1414
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/astrocytes-in-the-rostral-ventromedial-medulla-contribute-to-the-maintenance-of-orofacial-hyperalgesia-induced-by-late-removal-of-dental-occlusal-interference-n1414
[title] => Astrocytes in the rostral ventromedial medulla contribute to the maintenance of orofacial hyperalgesia induced by late removal of dental occlusal interference
[paragraph_crop] => Astrocytes in the rostral ventromedial medulla contribute to the maintenance of orofacial [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-05-27 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[31] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 31
[title] => Douleurs oro-faciales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-oro-faciales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1405] => Array
(
[id] => 1405
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/ferroptosis-is-involved-in-the-development-of-neuropathic-pain-and-allodynia-n1405
[title] => Ferroptosis is involved in the development of neuropathic pain and allodynia
[paragraph_crop] => Ferroptosis is involved in the development of neuropathic pain and allodynia
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-04-17 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1404] => Array
(
[id] => 1404
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/oral-supplementation-with-fish-cartilage-hydrolysate-accelerates-joint-function-recovery-in-rat-model-of-traumatic-knee-osteoarthritis-n1404
[title] => Oral supplementation with fish cartilage hydrolysate accelerates joint function recovery in rat model of traumatic knee osteoarthritis
[paragraph_crop] => Oral supplementation with fish cartilage hydrolysate accelerates joint function recovery in [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-04-10 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1387] => Array
(
[id] => 1387
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/extracellular-vesicles-released-from-hipsc-derived-mscs-attenuate-chronic-prostatitis-and-chronic-pelvic-pain-syndrome-in-rats-by-immunoregulation-n1387
[title] => Extracellular vesicles released from hiPSC-derived MSCs attenuate chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome in rats by immunoregulation
[paragraph_crop] => Extracellular vesicles released from hiPSC-derived MSCs attenuate chronic prostatitis and [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-03-20 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[32] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 32
[title] => Douleurs abdominales, ovaro-pelviennes et liées à l'endométriose
[link_rewrite] => douleurs-abdominales-ovaro-pelviennes-et-liees-a-l-endometriose
)
[98] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 98
[title] => Maladies auto-immunes
[link_rewrite] => Maladies-auto-immunes
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1391] => Array
(
[id] => 1391
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/preemptive-stem-cells-ameliorate-neuropathic-pain-in-rats--a-central-component-of-preemptive-analgesia-n1391
[title] => Preemptive Stem Cells Ameliorate Neuropathic Pain in Rats- A Central Component of Preemptive Analgesia
[paragraph_crop] => Preemptive Stem Cells Ameliorate Neuropathic Pain in Rats- A Central Component of Preemptive [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-02-16 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1381] => Array
(
[id] => 1381
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/inhibition-of-inflammatory-pain-and-cough-by-a-novel-charged-sodium-channel-blocker-n1381
[title] => Inhibition of inflammatory pain and cough by a novel charged sodium channel blocker
[paragraph_crop] => Inhibition of inflammatory pain and cough by a novel charged sodium channel blocker
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-02-08 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1360] => Array
(
[id] => 1360
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/anti-inflammatory-and-analgesic-effects-of-trpv1-polypeptide-modulator-aphc3-in-models-of-osteo-and-rheumatoid-arthritis-n1360
[title] => Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Effects of TRPV1 Polypeptide Modulator APHC3 in Models of Osteo-and Rheumatoid Arthritis
[paragraph_crop] => Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Effects of TRPV1 Polypeptide Modulator APHC3 in Models of [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2021-01-17 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1349] => Array
(
[id] => 1349
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/inhibiting-cough-by-silencing-large-pore-expressing-airway-sensory-neurons-with-a-charged-sodium-channel-blocker-2-n1349
[title] => Inhibiting cough by silencing large pore-expressing airway sensory neurons with a charged sodium channel blocker 2
[paragraph_crop] => Inhibiting cough by silencing large pore-expressing airway sensory neurons with a charged [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-12-07 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1347] => Array
(
[id] => 1347
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/the-adjuvant-induced-rat-model-of-monoarthritis--welfare-implications-and-possible-refinement-strategies-n1347
[title] => The adjuvant-induced rat model of monoarthritis- welfare implications and possible refinement strategies
[paragraph_crop] => The adjuvant-induced rat model of monoarthritis: welfare implications and possible refinement [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-12-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1320] => Array
(
[id] => 1320
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/albiflorin-attenuates-mood-disorders-under-neuropathic-pain-state-by-suppressing-the-hippocampal-nlrp3-inflammasome-activation-during-chronic-constriction-injury-n1320
[title] => Albiflorin Attenuates Mood Disorders Under Neuropathic Pain State By Suppressing The Hippocampal NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation During Chronic Constriction Injury
[paragraph_crop] => Albiflorin Attenuates Mood Disorders Under Neuropathic Pain State By Suppressing The [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-09-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[56] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 56
[title] => Anxiété
[link_rewrite] => Anxiété
)
[57] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 57
[title] => Dépression
[link_rewrite] => Depression
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1308] => Array
(
[id] => 1308
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/repeated-intrathecal-administration-of-ropivacaine-hydrochloride-induces-apoptosis-via-up-regulating-of-fas-and-fasl-expression-in-the-rat-spinal-cord-n1308
[title] => Repeated Intrathecal Administration of Ropivacaine Hydrochloride Induces Apoptosis Via Up-Regulating of Fas and FasL Expression in the Rat Spinal Cord
[paragraph_crop] => Repeated Intrathecal Administration of Ropivacaine Hydrochloride Induces Apoptosis Via [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-09-25 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[39] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 39
[title] => Moelle épinière
[link_rewrite] => Moelle-epiniere
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1303] => Array
(
[id] => 1303
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/rational-design-of-new-multitarget-histamine-h3-receptor-ligands-as-potential-candidates-for-treatment-of-alzheimers-disease-n1303
[title] => Rational design of new multitarget histamine H3 receptor ligands as potential candidates for treatment of AlzheimerÕs disease
[paragraph_crop] => Rational design of new multitarget histamine H3 receptor ligands as potential candidates for [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-08-21 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[46] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 46
[title] => Maladie d'Alzheimer
[link_rewrite] => maladie-d-alzheimer
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1296] => Array
(
[id] => 1296
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/alterations-of-distributed-neuronal-network-oscillations-during-acute-pain-in-freely-moving-mice-n1296
[title] => Alterations of distributed neuronal network oscillations during acute pain in freely-moving mice
[paragraph_crop] => Alterations of distributed neuronal network oscillations during acute pain in freely-moving mice
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-08-11 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1283] => Array
(
[id] => 1283
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/ultrafast-ultrasound-imaging-pattern-analysis-reveals-distinctive-dynamic-brain-states-and-potent-sub-network-alterations-in-arthritic-animals-n1283
[title] => Ultrafast ultrasound imaging pattern analysis reveals distinctive dynamic brain states and potent sub-network alterations in arthritic animals
[paragraph_crop] => Ultrafast ultrasound imaging pattern analysis reveals distinctive dynamic brain states and [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-06-26 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
)
)
[1280] => Array
(
[id] => 1280
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/the-effect-of-pirfenidone-on-rat-chronic-prostatitis-and-chronic-pelvic-pain-syndrome-and-its-mechanisms-n1280
[title] => The effect of pirfenidone on rat chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome and its mechanisms
[paragraph_crop] => The effect of pirfenidone on rat chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome and its mechanisms
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-06-22 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
)
)
[1278] => Array
(
[id] => 1278
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/a-novel-view-of-the-problem-of-osteoarthritis-in-experimental-rat-model-n1278
[title] => A novel view of the problem of Osteoarthritis in experimental rat model
[paragraph_crop] => A novel view of the problem of Osteoarthritis in experimental rat model
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-06-19 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
)
)
[1274] => Array
(
[id] => 1274
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/the-role-of-cashew--anacardium-occidentale-l---nuts-on-an-experimental-model-of-painful-degenerative-joint-disease-n1274
[title] => The Role of Cashew -Anacardium occidentale L-- Nuts on an Experimental Model of Painful Degenerative Joint Disease
[paragraph_crop] => The Role of Cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) Nuts on an Experimental Model of Painful [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-06-10 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
)
)
[1259] => Array
(
[id] => 1259
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/analgesic-and-neuroprotective-effects-of-electroacupuncture-in-a-dental-pulp-injury-model-n1259
[title] => Analgesic and Neuroprotective Effects of Electroacupuncture in a Dental Pulp Injury Model
[paragraph_crop] => Analgesic and Neuroprotective Effects of Electroacupuncture in a Dental Pulp Injury Model
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-04-09 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1250] => Array
(
[id] => 1250
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/neuroheal-treatment-alleviates-neuropathic-pain-and-enhances-sensory-axon-regeneration-n1250
[title] => NeuroHeal Treatment Alleviates Neuropathic Pain and Enhances Sensory Axon Regeneration
[paragraph_crop] => NeuroHeal Treatment Alleviates Neuropathic Pain and Enhances Sensory Axon Regeneration
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-03-27 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1251] => Array
(
[id] => 1251
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/effect-of-artesunate-on-leishmania-amazonesis-induced-neuroinflammation-and-nociceptive-behavior-in-male-balb-and-c-mice-n1251
[title] => Effect of Artesunate on Leishmania Amazonesis Induced Neuroinflammation and Nociceptive Behavior in Male Balb and C Mice
[paragraph_crop] => Effect of Artesunate on Leishmania Amazonesis Induced Neuroinflammation and Nociceptive [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-03-27 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[99] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 99
[title] => Infection
[link_rewrite] => Infection
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1249] => Array
(
[id] => 1249
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/dim-light-at-night-exposure-induces-cold-hyperalgesia-and-mechanical-allodynia-in-male-mice-n1249
[title] => Dim light at night exposure induces cold hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia in male mice
[paragraph_crop] => Dim light at night exposure induces cold hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia in male mice
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-03-19 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1247] => Array
(
[id] => 1247
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/gabaergic-modulation-of-secondary-hyperalgesia--a-randomized-controlled-4way-crossover-trial-with-the-alpha2subunit-preferring-gaba-positive-allosteric-modulator--ndesmethylclobazam-in-healthy-volunteers--n1247
[title] => GABAergic modulation of secondary hyperalgesia- A randomized controlled 4_way crossover trial with the alpha2_subunit preferring GABA positive allosteric modulator- N_desmethyl_clobazam in healthy volunteers
[paragraph_crop] => GABAergic modulation of secondary hyperalgesia: A randomized controlled 4_way crossover trial [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-03-14 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1243] => Array
(
[id] => 1243
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/disabling-phosphorylation-at-the-homer-ligand-of-the-metabotropic-glutamate-receptor-5-alleviates-complete-freunds-adjuvant-induced-inflammatory-pain-n1243
[title] => Disabling phosphorylation at the homer ligand of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 alleviates complete Freund's adjuvant-induced inflammatory pain
[paragraph_crop] => Disabling phosphorylation at the homer ligand of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-03-07 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1210] => Array
(
[id] => 1210
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/n-acetyl-l-cysteine-reduces-leishmania-amazonensis-induced-inflammation-in-balb-and-c-mice-n1210
[title] => N-acetyl-L-cysteine reduces Leishmania amazonensis-induced inflammation in BALB and c mice
[paragraph_crop] => N-acetyl-L-cysteine reduces Leishmania amazonensis-induced inflammation in BALB/c mice
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-01-13 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[96] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 96
[title] => Autres pathologies
[link_rewrite] => Autres-pathologies
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[25] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 25
[title] => Thematiques diverses
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-diverses
)
)
)
[1184] => Array
(
[id] => 1184
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/tanshinone-iia-contributes-to-the-pathogenesis-of-endometriosis-via-renin-angiotensin-system-by-regulating-the-dorsal-root-ganglion-axon-sprouting-n1184
[title] => Tanshinone IIA contributes to the pathogenesis of endometriosis via renin angiotensin system by regulating the dorsal root ganglion axon sprouting
[paragraph_crop] => Tanshinone IIA contributes to the pathogenesis of endometriosis via renin angiotensin system [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2020-01-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1191] => Array
(
[id] => 1191
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/melatonin-plus-folic-acid-treatment-ameliorates-reserpine-induced-fibromyalgia--an-evaluation-of-pain--oxidative-stress--and-inflammation-n1191
[title] => Melatonin Plus Folic Acid Treatment Ameliorates Reserpine-Induced Fibromyalgia- An Evaluation of Pain- Oxidative Stress- and Inflammation
[paragraph_crop] => Melatonin Plus Folic Acid Treatment Ameliorates Reserpine-Induced Fibromyalgia: An Evaluation [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-12-06 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1194] => Array
(
[id] => 1194
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/a-longitudinal-model-of-periprosthetic-joint-infection-in-the-rat-n1194
[title] => A longitudinal model of periprosthetic joint infection in the rat
[paragraph_crop] => A longitudinal model of periprosthetic joint infection in the rat
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-12-06 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[33] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 33
[title] => Douleurs post-opératoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-post-opératoires
)
[99] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 99
[title] => Infection
[link_rewrite] => Infection
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1181] => Array
(
[id] => 1181
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/perioperative-intravenous-lowdose-ketamine-for-neuropathic-pain-after-major-lower-back-surgery--a-randomized--placebocontrolled-study-n1181
[title] => Perioperative intravenous low_dose ketamine for neuropathic pain after major lower back surgery- A randomized- placebo_controlled study
[paragraph_crop] => Perioperative intravenous low_dose ketamine for neuropathic pain after major lower back [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-11-19 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[33] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 33
[title] => Douleurs post-opératoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-post-opératoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1169] => Array
(
[id] => 1169
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/highly-bioavailable-curcumin-powder-suppresses-articular-cartilage-damage-in-rats-with-mono-iodoacetate--mia--induced-osteoarthritis-n1169
[title] => Highly bioavailable curcumin powder suppresses articular cartilage damage in rats with mono-iodoacetate -MIA--induced osteoarthritis
[paragraph_crop] => Highly bioavailable curcumin powder suppresses articular cartilage damage in rats with [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-10-05 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1134] => Array
(
[id] => 1134
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/minocycline-attenuates-the-development-of-diabetic-neuropathy-by-modulating-dream-and-bdnf-protein-expression-in-rat-spinal-cord-n1134
[title] => Minocycline attenuates the development of diabetic neuropathy by modulating DREAM and BDNF protein expression in rat spinal cord
[paragraph_crop] => Minocycline attenuates the development of diabetic neuropathy by modulating DREAM and BDNF [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-05-18 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1112] => Array
(
[id] => 1112
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/ipse--a-parasite-derived-host-immunomodulatory-protein--is-a-potential-therapeutic-for-hemorrhagic-cystitis-n1112
[title] => IPSE- a parasite-derived host immunomodulatory protein- is a potential therapeutic for hemorrhagic cystitis
[paragraph_crop] => IPSE, a parasite-derived host immunomodulatory protein, is a potential therapeutic for [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-02-20 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[90] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 90
[title] => Cancer
[link_rewrite] => Cancer
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[1108] => Array
(
[id] => 1108
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/cholesterol-depletion-regulates-axonal-growth-and-enhances-central-and-peripheral-nerve-regeneration-n1108
[title] => Cholesterol Depletion Regulates Axonal Growth and Enhances Central and Peripheral Nerve Regeneration
[paragraph_crop] => Cholesterol Depletion Regulates Axonal Growth and Enhances Central and Peripheral Nerve Regeneration
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-02-12 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[1104] => Array
(
[id] => 1104
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/bexarotent-attenuated-cci-induced-spinal-neuroinflammation-and-neuropathic-pain-by-targeting-mkp-1-n1104
[title] => Bexarotent attenuated CCI-induced spinal neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain by targeting MKP-1
[paragraph_crop] => Bexarotent attenuated CCI-induced spinal neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain by targeting MKP-1
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2019-01-19 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1091] => Array
(
[id] => 1091
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/increased-nociceptive-responses-in-streptozotocin-induced-diabetic-rats-and-the-related-expression-of-spinal-nr2b-subunit-of-n-methyl-d-aspartate-receptors-n1091
[title] => Increased Nociceptive Responses in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats and the Related Expression of Spinal NR2B Subunit of N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptors
[paragraph_crop] => Increased Nociceptive Responses in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats and the Related [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-11-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[81] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 81
[title] => Diabète, Insuline & Glucose
[link_rewrite] => Diabète-Insuline-Glucose
)
[23] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 23
[title] => Métabolisme
[link_rewrite] => Metabolisme
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1087] => Array
(
[id] => 1087
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/may-a-sigma1-antagonist-improve-neuropathic-signs-induced-by-cisplatin-and-vincristine-in-rats-n1087
[title] => May a sigma_1 antagonist improve neuropathic signs induced by cisplatin and vincristine in rats?
[paragraph_crop] => May a sigma_1 antagonist improve neuropathic signs induced by cisplatin and vincristine in rats?
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-10-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[100] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 100
[title] => Fonction cardiaque
[link_rewrite] => Fonction-cardiaque
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1018] => Array
(
[id] => 1018
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/hydrogen-rich-saline-activated-autophagy-via-hif-1-pathways-in-neuropathic-pain-model-n1018
[title] => Hydrogen-Rich Saline Activated Autophagy via HIF-1_ Pathways in Neuropathic Pain Model
[paragraph_crop] => Hydrogen-Rich Saline Activated Autophagy via HIF-1_ Pathways in Neuropathic Pain Model
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-05-17 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1008] => Array
(
[id] => 1008
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/on-the-use-of-parylene-c-polymer-as-substrate-for-peripheral-nerve-electrodes-n1008
[title] => On the use of Parylene C polymer as substrate for peripheral nerve electrodes
[paragraph_crop] => On the use of Parylene C polymer as substrate for peripheral nerve electrodes
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-04-13 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[93] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 93
[title] => Inflammation
[link_rewrite] => Inflammation
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[1044] => Array
(
[id] => 1044
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/transdermal-fentanyl-solution-provides-long-term-analgesia-in-the-hind-paw-incisional-model-of-postoperative-pain-in-male-rats-n1044
[title] => Transdermal Fentanyl Solution Provides Long-term Analgesia in the Hind-paw Incisional Model of Postoperative Pain in Male Rats
[paragraph_crop] => Transdermal Fentanyl Solution Provides Long-term Analgesia in the Hind-paw Incisional Model of [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-03-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[33] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 33
[title] => Douleurs post-opératoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-post-opératoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[967] => Array
(
[id] => 967
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/role-of-medullary-astroglial-glutamine-synthesis-in-tooth-pulp-hypersensitivity-associated-with-frequent-masseter-muscle-contraction--n967
[title] => Role of medullary astroglial glutamine synthesis in tooth pulp hypersensitivity associated with frequent masseter muscle contraction
[paragraph_crop] => Role of medullary astroglial glutamine synthesis in tooth pulp hypersensitivity associated [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-02-15 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[31] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 31
[title] => Douleurs oro-faciales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-oro-faciales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[970] => Array
(
[id] => 970
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/schwann-cells-and-mesenchymal-stem-cells-in-laminin--or-fibronectin-aligned-matrices-and-regeneration-across-a-critical-size-defect-of-15-mm-in-the-rat-sciatic-nerve-n970
[title] => Schwann cells and mesenchymal stem cells in laminin- or fibronectin-aligned matrices and regeneration across a critical size defect of 15 mm in the rat sciatic nerve
[paragraph_crop] => Schwann cells and mesenchymal stem cells in laminin- or fibronectin-aligned matrices and [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-01-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[981] => Array
(
[id] => 981
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/monoaminergic-descending-pathways-contribute-to-modulation-of-neuropathic-pain-by-increasing-intensity-treadmill-exercise-after-peripheral-nerve-injury-n981
[title] => Monoaminergic descending pathways contribute to modulation of neuropathic pain by increasing-intensity treadmill exercise after peripheral nerve injury
[paragraph_crop] => Monoaminergic descending pathways contribute to modulation of neuropathic pain by [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2018-01-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[101] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 101
[title] => Exercice & Endurance
[link_rewrite] => Exercice-et-Endurance
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[942] => Array
(
[id] => 942
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/time-course-study-of-long-term-biocompatibility-and-foreign-body-reaction-to-intraneural-polyimide-based-implants-n942
[title] => Time course study of long-term biocompatibility and foreign body reaction to intraneural polyimide-based implants
[paragraph_crop] => Time course study of long-term biocompatibility and foreign body reaction to intraneural [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2017-11-18 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[931] => Array
(
[id] => 931
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/cxcr4-signaling-contributes-to-alveolar-bone-resorption-in-porphyromonas-gingivalis-induced-periodontitis-in-mice--n931
[title] => CXCR4 signaling contributes to alveolar bone resorption in Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced periodontitis in mice
[paragraph_crop] => CXCR4 signaling contributes to alveolar bone resorption in Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2017-10-31 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[99] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 99
[title] => Infection
[link_rewrite] => Infection
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[975] => Array
(
[id] => 975
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/group-i-metabotropic-glutamate-receptor-plasticity-after-peripheral-inflammation-alters-nociceptive-transmission-in-the-dorsal-horn-of-the-spinal-cord-in-adult-rats-n975
[title] => Group I metabotropic glutamate receptor plasticity after peripheral inflammation alters nociceptive transmission in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord in adult rats
[paragraph_crop] => Group I metabotropic glutamate receptor plasticity after peripheral inflammation alters [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2017-09-25 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[898] => Array
(
[id] => 898
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/antinociceptive--antiallodynic-and-antihyperalgesic-effects-of-the-5-ht1a-receptor-selective-agonist--nlx-112-in-mouse-models-of-pain-n898
[title] => Antinociceptive- antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic effects of the 5-HT1A receptor selective agonist- NLX-112 in mouse models of pain
[paragraph_crop] => Antinociceptive, antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic effects of the 5-HT1A receptor selective [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2017-07-22 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[90] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 90
[title] => Cancer
[link_rewrite] => Cancer
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[45] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 45
[title] => Maladie de Parkinson
[link_rewrite] => Maladie-de-Parkinson
)
[12] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 12
[title] => Neurodégénérescence
[link_rewrite] => Neurodegenerescence
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[1144] => Array
(
[id] => 1144
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/5ht-in-the-dorsal-raphe-nucleus-is-involved-in-the-effects-of-100hz-electroacupuncture-on-the-paindepression-dyad-in-rats-n1144
[title] => 5_HT in the dorsal raphe nucleus is involved in the effects of 100_Hz electro_acupuncture on the pain_depression dyad in rats
[paragraph_crop] => 5_HT in the dorsal raphe nucleus is involved in the effects of 100_Hz electro_acupuncture on [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2017-05-19 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[57] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 57
[title] => Dépression
[link_rewrite] => Depression
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[15] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 15
[title] => Troubles de l'humeur
[link_rewrite] => Troubles-de-l-humeur
)
)
)
[882] => Array
(
[id] => 882
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/cav1--2-and-cav1--3-ltype-calcium-channels-independently-control-shortand-longterm-sensitization-to-pain-n882
[title] => Cav1- 2 and Cav1- 3 l‐type calcium channels independently control short‐and long‐term sensitization to pain
[paragraph_crop] => Cav1. 2 and Cav1. 3 l‐type calcium channels independently control short‐and long‐term sensi [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2016-05-27 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[877] => Array
(
[id] => 877
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/inhibition-of-the-neuronal-nfb-pathway-attenuates-bortezomib-induced-neuropathy-in-a-mouse-model--n877
[title] => Inhibition of the neuronal NFκB pathway attenuates bortezomib-induced neuropathy in a mouse model-
[paragraph_crop] => Inhibition of the neuronal NFκB pathway attenuates bortezomib-induced neuropathy in a mouse model.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2016-05-19 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[828] => Array
(
[id] => 828
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/effect-of-dexmedetomidine-and-cold-stress-in-a-rat-model-of-neuropathic-pain--role-of-interleukin-6-and-tumor-necrosis-factor--n828
[title] => Effect of dexmedetomidine and cold stress in a rat model of neuropathic pain- Role of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α
[paragraph_crop] => Effect of dexmedetomidine and cold stress in a rat model of neuropathic pain: Role of [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2016-04-05 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[735] => Array
(
[id] => 735
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/in-vitro-and-noninvasive-in-vivo-effects-of-the-cannabinoid1-receptor-agonist-am841-on-gastrointestinal-motor-function-in-the-rat-n735
[title] => In vitro and non?invasive in vivo effects of the cannabinoid?1 receptor agonist AM841 on gastrointestinal motor function in the rat
[paragraph_crop] => In vitro and non?invasive in vivo effects of the cannabinoid?1 receptor agonist AM841 on [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-09-20 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[32] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 32
[title] => Douleurs abdominales, ovaro-pelviennes et liées à l'endométriose
[link_rewrite] => douleurs-abdominales-ovaro-pelviennes-et-liees-a-l-endometriose
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[98] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 98
[title] => Maladies auto-immunes
[link_rewrite] => Maladies-auto-immunes
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[775] => Array
(
[id] => 775
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/3-4--3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl--piperazin-1-yl-dihydrofuran-2-one-and-pregabalin-attenuate-tactile-allodynia-in-the-mouse-model-of-chronic-constriction-injury-n775
[title] => 3-[4--3-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl--piperazin-1-yl]-dihydrofuran-2-one and pregabalin attenuate tactile allodynia in the mouse model of chronic constriction injury
[paragraph_crop] => 3-[4--3-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl--piperazin-1-yl]-dihydrofuran-2-one and pregabalin attenuate tactile
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-09-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
)
)
[730] => Array
(
[id] => 730
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/early-increasing-intensity-treadmill-exercise-reduces-neuropathic-pain-by-preventing-nociceptor-collateral-sprouting-and-disruption-of-chloride-cotransporters-homeostasis-after-peripheral-nerve-injury-n730
[title] => Early increasing-intensity treadmill exercise reduces neuropathic pain by preventing nociceptor collateral sprouting and disruption of chloride cotransporters homeostasis after peripheral nerve injury
[paragraph_crop] => Early increasing-intensity treadmill exercise reduces neuropathic pain by preventing [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-09-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[808] => Array
(
[id] => 808
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/changes-of-voltage-gated-sodium-channels-in-sensory-nerve-regeneration-and-neuropathic-pain-models-n808
[title] => Changes of voltage-gated sodium channels in sensory nerve regeneration and neuropathic pain models
[paragraph_crop] => Changes of voltage-gated sodium channels in sensory nerve regeneration and neuropathic pain models
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-06-17 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[774] => Array
(
[id] => 774
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/inflammatory-pain-memory-facilitates-occlusal-interferenceinduced-masticatory-muscle-hyperalgesia-in-rats-n774
[title] => Inflammatory pain memory facilitates occlusal interference?induced masticatory muscle hyperalgesia in rats
[paragraph_crop] => Inflammatory pain memory facilitates occlusal interference?induced masticatory muscle [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-05-26 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[31] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 31
[title] => Douleurs oro-faciales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-oro-faciales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[777] => Array
(
[id] => 777
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/nkcc1-activation-is-required-for-myelinated-sensory-neurons-regeneration-through-jnk-dependent-pathway-n777
[title] => NKCC1 Activation Is Required for Myelinated Sensory Neurons Regeneration through JNK-Dependent Pathway
[paragraph_crop] => NKCC1 Activation Is Required for Myelinated Sensory Neurons Regeneration through JNK-Dependent [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-05-13 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[765] => Array
(
[id] => 765
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/biocompatibility-evaluation-of-parylene-c-and-polyimide-as-substrates-for-peripheral-nerve-interfaces-n765
[title] => Biocompatibility evaluation of parylene C and polyimide as substrates for peripheral nerve interfaces
[paragraph_crop] => Biocompatibility evaluation of parylene C and polyimide as substrates for peripheral nerve [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-04-22 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[661] => Array
(
[id] => 661
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/gabaergic-modulation-in-central-sensitization-in-humans--a-randomized-placebo-controlled-pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic-study-comparing-clobazam-with-clonazepam-in-healthy-volunteers--n661
[title] => GABAergic modulation in central sensitization in humans- a randomized placebo-controlled pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic study comparing clobazam with clonazepam in healthy volunteers-
[paragraph_crop] => GABAergic modulation in central sensitization in humans: a randomized placebo-controlled [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-03-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[95] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 95
[title] => Pharmacologie
[link_rewrite] => Pharmacologie
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[672] => Array
(
[id] => 672
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/antinociceptive-activity-of-transient-receptor-potential-channel-trpv1--trpa1--and-trpm8-antagonists-in-neurogenic-and-neuropathic-pain-models-in-mice-n672
[title] => Antinociceptive activity of transient receptor potential channel TRPV1- TRPA1- and TRPM8 antagonists in neurogenic and neuropathic pain models in mice
[paragraph_crop] => Antinociceptive activity of transient receptor potential channel TRPV1, TRPA1, and TRPM8 [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-03-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[806] => Array
(
[id] => 806
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/effects-of-electroacupuncture-with-dominant-frequency-at-sp-6-and-st-36-based-on-meridian-theory-on-pain-depression-dyad-in-rats-n806
[title] => Effects of Electroacupuncture with Dominant Frequency at SP 6 and ST 36 Based on Meridian Theory on Pain-depression Dyad in Rats
[paragraph_crop] => Effects of Electroacupuncture with Dominant Frequency at SP 6 and ST 36 Based on Meridian [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-02-16 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[35] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 35
[title] => Douleurs émotionnelles
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-émotionnelles
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[653] => Array
(
[id] => 653
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/a-three-dimensional-self-opening-intraneural-peripheral-interface--seline--n653
[title] => A three-dimensional self-opening intraneural peripheral interface -SELINE-
[paragraph_crop] => A three-dimensional self-opening intraneural peripheral interface (SELINE)
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-02-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[658] => Array
(
[id] => 658
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/involvement-of-trpv1-and-trpa1-in-incisional-intraoral-and-extraoral-pain-n658
[title] => Involvement of TRPV1 and TRPA1 in Incisional Intraoral and Extraoral Pain
[paragraph_crop] => Involvement of TRPV1 and TRPA1 in Incisional Intraoral and Extraoral Pain
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2015-01-09 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[31] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 31
[title] => Douleurs oro-faciales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-oro-faciales
)
[33] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 33
[title] => Douleurs post-opératoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-post-opératoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[667] => Array
(
[id] => 667
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/nociceptive-spinal-cord-neurons-of-laminae-i-iii-exhibit-oxidative-stress-damage-during-diabetic-neuropathy-which-is-prevented-by-early-antioxidant-treatment-with-epigallocatechin-gallate--egcg--n667
[title] => Nociceptive spinal cord neurons of laminae I-III exhibit oxidative stress damage during diabetic neuropathy which is prevented by early antioxidant treatment with epigallocatechin-gallate -EGCG-
[paragraph_crop] => Nociceptive spinal cord neurons of laminae I-III exhibit oxidative stress damage during [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-12-16 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[23] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 23
[title] => Métabolisme
[link_rewrite] => Metabolisme
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[86] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 86
[title] => Stress oxydant
[link_rewrite] => Stress-oxydant
)
)
)
[674] => Array
(
[id] => 674
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/tubulization-with-chitosan-guides-for-the-repair-of-long-gap-peripheral-nerve-injury-in-the-rat-n674
[title] => Tubulization with chitosan guides for the repair of long gap peripheral nerve injury in the rat
[paragraph_crop] => Tubulization with chitosan guides for the repair of long gap peripheral nerve injury in the rat
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-12-04 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[690] => Array
(
[id] => 690
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/bdnf-dependent-plasticity-induced-by-peripheral-inflammation-in-the-primary-sensory-and-the-cingulate-cortex-triggers-cold-allodynia-and-reveals-a-major-role-for-endogenous-bdnf-as-a-tuner-of-the-affective-aspect-of-pain-n690
[title] => BDNF-dependent plasticity induced by peripheral inflammation in the primary sensory and the cingulate cortex triggers cold allodynia and reveals a major role for endogenous BDNF as a tuner of the affective aspect of pain
[paragraph_crop] => BDNF-dependent plasticity induced by peripheral inflammation in the primary sensory and the [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-10-29 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[35] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 35
[title] => Douleurs émotionnelles
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-émotionnelles
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[629] => Array
(
[id] => 629
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/analgesic-effects-of-clinically-used-compounds-in-novel-mouse-models-of-polyneuropathy-induced-by-oxaliplatin-and-cisplatin-n629
[title] => Analgesic effects of clinically used compounds in novel mouse models of polyneuropathy induced by oxaliplatin and cisplatin
[paragraph_crop] => Analgesic effects of clinically used compounds in novel mouse models of polyneuropathy induced [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-10-16 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[697] => Array
(
[id] => 697
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/buccal-acetaminophen-provides-fast-analgesia--two-randomized-clinical-trials-in-healthy-volunteers-n697
[title] => Buccal acetaminophen provides fast analgesia- two randomized clinical trials in healthy volunteers
[paragraph_crop] => Buccal acetaminophen provides fast analgesia: two randomized clinical trials in healthy volunteers
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-09-26 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[95] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 95
[title] => Pharmacologie
[link_rewrite] => Pharmacologie
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[586] => Array
(
[id] => 586
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/monoarthritis-induced-emotional-and-cognitive-impairments-in-rats-are-sensitive-to-low-systemic-doses-or-intra-amygdala-injections-of-morphine-n586
[title] => Monoarthritis-induced emotional and cognitive impairments in rats are sensitive to low systemic doses or intra-amygdala injections of morphine
[paragraph_crop] => Monoarthritis-induced emotional and cognitive impairments in rats are sensitive to low [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-04-18 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[16] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 16
[title] => Autres pathologies
[link_rewrite] => Autres-pathologies
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[60] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 60
[title] => Performances cognitives
[link_rewrite] => Performances-cognitives
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[589] => Array
(
[id] => 589
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/face-to-face-comparison-of-the-predictive-validity-of-two-models-of-neuropathic-pain-in-the-rat--analgesic-activity-of-pregabalin--tramadol-and-duloxetine-n589
[title] => Face-to-face comparison of the predictive validity of two models of neuropathic pain in the rat- Analgesic activity of pregabalin- tramadol and duloxetine
[paragraph_crop] => Face-to-face comparison of the predictive validity of two models of neuropathic pain in the [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-04-12 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[590] => Array
(
[id] => 590
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/antiallodynic-and-antihyperalgesic-activity-of-3-4--3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl--piperazin-1-yl-dihydrofuran-2-one-compared-to-pregabalin-in-chemotherapy-induced-neuropathic-pain-in-mice-n590
[title] => Antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic activity of 3-[4--3-trifluoromethyl-phenyl--piperazin-1-yl]-dihydrofuran-2-one compared to pregabalin in chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain in mice
[paragraph_crop] => Antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic activity of [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-04-12 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[593] => Array
(
[id] => 593
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/bone-marrow-mesenchymal-stromal-cells-and-olfactory-ensheathing-cells-transplantation-after-spinal-cord-injury--a-morphological-and-functional-comparison-in-rats-n593
[title] => Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells and olfactory ensheathing cells transplantation after spinal cord injury – a morphological and functional comparison in rats
[paragraph_crop] => Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells and olfactory ensheathing cells transplantation after [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-03-18 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[39] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 39
[title] => Moelle épinière
[link_rewrite] => Moelle-epiniere
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[594] => Array
(
[id] => 594
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/molecular-mechanisms-underlying-the-enhanced-analgesic-effect-of-oxycodone-compared-to-morphine-in-chemotherapy-induced-neuropathic-pain--n594
[title] => Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Enhanced Analgesic Effect of Oxycodone Compared to Morphine in Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain
[paragraph_crop] => Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Enhanced Analgesic Effect of Oxycodone Compared to [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-03-11 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[95] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 95
[title] => Pharmacologie
[link_rewrite] => Pharmacologie
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[599] => Array
(
[id] => 599
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/assessment-of-sensory-thresholds-and-nociceptive-fiber-growth-after-sciatic-nerve-injury-reveals-the-differential-contribution-of-collateral-reinnervation-and-nerve-regeneration-to-neuropathic-pain-n599
[title] => Assessment of sensory thresholds and nociceptive fiber growth after sciatic nerve injury reveals the differential contribution of collateral reinnervation and nerve regeneration to neuropathic pain
[paragraph_crop] => Assessment of sensory thresholds and nociceptive fiber growth after sciatic nerve injury [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-02-16 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[602] => Array
(
[id] => 602
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/therapeutic-effects-of-thymoquinone-in-a-model-of-neuropathic-pain--n602
[title] => Therapeutic Effects of Thymoquinone in a Model of Neuropathic Pain
[paragraph_crop] => Therapeutic Effects of Thymoquinone in a Model of Neuropathic Pain
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2014-02-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[95] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 95
[title] => Pharmacologie
[link_rewrite] => Pharmacologie
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[499] => Array
(
[id] => 499
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/a-polyamine-deficient-diet-prevents-oxaliplatin-induced-acute-cold-and-mechanical-hypersensitivity-in-rats-n499
[title] => A Polyamine-Deficient Diet Prevents Oxaliplatin-Induced Acute Cold and Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats
[paragraph_crop] => A Polyamine-Deficient Diet Prevents Oxaliplatin-Induced Acute Cold and Mechanical [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-11-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[48] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 48
[title] => Perception du chaud et du froid
[link_rewrite] => Perception-du-chaud-et-du-froid
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[13] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 13
[title] => Système sensoriel
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-sensoriel
)
)
)
[537] => Array
(
[id] => 537
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/structural-and-molecular-alterations-of-primary-afferent-fibres-in-the-spinal-dorsal-horn-in-vincristine-induced-neuropathy-in-rat-n537
[title] => Structural and Molecular Alterations of Primary Afferent Fibres in the Spinal Dorsal Horn in Vincristine-Induced Neuropathy in Rat
[paragraph_crop] => Structural and Molecular Alterations of Primary Afferent Fibres in the Spinal Dorsal Horn in [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-11-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[527] => Array
(
[id] => 527
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/phagocytic-microglial-phenotype-induced-by-glibenclamide-improves-functional-recovery-but-worsens-hyperalgesia-after-spinal-cord-injury-in-adult-rats-n527
[title] => Phagocytic microglial phenotype induced by glibenclamide improves functional recovery but worsens hyperalgesia after spinal cord injury in adult rats
[paragraph_crop] => Phagocytic microglial phenotype induced by glibenclamide improves functional recovery but [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-10-02 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[521] => Array
(
[id] => 521
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/an-animal-model-of-oxaliplatin-induced-cold-allodynia-reveals-a-crucial-role-for-nav1-6-in-peripheral-pain-pathways-n521
[title] => An animal model of oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia reveals a crucial role for Nav1-6 in peripheral pain pathways
[paragraph_crop] => An animal model of oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia reveals a crucial role for Nav1.6 in [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-09-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[558] => Array
(
[id] => 558
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/local-and-remote-immune-mediated-inflammation-after-mild-peripheral-nerve-compression-in-rats--n558
[title] => Local and remote immune-mediated inflammation after mild peripheral nerve compression in rats-
[paragraph_crop] => Local and remote immune-mediated inflammation after mild peripheral nerve compression in rats.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-07-31 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[546] => Array
(
[id] => 546
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/unexpected-association-of-the-inhibitory-neuroligin-2-with-excitatory-psd95-in-neuropathic-pain-n546
[title] => Unexpected association of the “inhibitory” neuroligin 2 with excitatory PSD95 in neuropathic pain
[paragraph_crop] => Unexpected association of the “inhibitory” neuroligin 2 with excitatory PSD95 in neuropathic pain
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-07-29 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[486] => Array
(
[id] => 486
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/bilateral-lesions-of-the-nigrostriatal-pathways-are-associated-with-chronic-mechanical-pain-hypersensitivity-in-rats-n486
[title] => Bilateral lesions of the nigrostriatal pathways are associated with chronic mechanical pain hypersensitivity in rats
[paragraph_crop] => Bilateral lesions of the nigrostriatal pathways are associated with chronic mechanical pain [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-05-15 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[45] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 45
[title] => Maladie de Parkinson
[link_rewrite] => Maladie-de-Parkinson
)
[12] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 12
[title] => Neurodégénérescence
[link_rewrite] => Neurodegenerescence
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[479] => Array
(
[id] => 479
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/plastic-changes-in-lumbar-segments-after-thoracic-spinal-cord-injuries-in-adult-rats--an-integrative-view-of-spinal-nociceptive-dysfunctions-n479
[title] => Plastic changes in lumbar segments after thoracic spinal cord injuries in adult rats- An integrative view of spinal nociceptive dysfunctions
[paragraph_crop] => Plastic changes in lumbar segments after thoracic spinal cord injuries in adult rats: An [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-04-23 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[39] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 39
[title] => Moelle épinière
[link_rewrite] => Moelle-epiniere
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[465] => Array
(
[id] => 465
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/characterization-of-cannabinoid-induced-relief-of-neuropathic-pain-in-a-rat-model-of-cisplatin-induced-neuropathy-n465
[title] => Characterization of cannabinoid-induced relief of neuropathic pain in a rat model of cisplatin-induced neuropathy
[paragraph_crop] => Characterization of cannabinoid-induced relief of neuropathic pain in a rat model of [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-04-16 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[459] => Array
(
[id] => 459
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/acute-delivery-of-epha4-fc-improves-functional-recovery-after-contusive-spinal-cord-injury-in-rats--n459
[title] => Acute delivery of EphA4-Fc improves functional recovery after contusive spinal cord injury in rats
[paragraph_crop] => Acute delivery of EphA4-Fc improves functional recovery after contusive spinal cord injury in rats
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-04-04 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[39] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 39
[title] => Moelle épinière
[link_rewrite] => Moelle-epiniere
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[442] => Array
(
[id] => 442
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/differential-effects-of-activity-dependent-treatments-on-axonal-regeneration-and-neuropathic-pain-after-peripheral-nerve-injury-n442
[title] => Differential effects of activity dependent treatments on axonal regeneration and neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury
[paragraph_crop] => Differential effects of activity dependent treatments on axonal regeneration and neuropathic [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2013-02-28 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[445] => Array
(
[id] => 445
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/metabotropic-glutamate-receptor-5-contributes-to-inflammatory-tongue-pain-via-extracellular-signalregulated-kinase-signaling-in-the-trigeminal-spinal-subnucleus-caudalis-and-upper-cervical-spinal-cord-n445
[title] => Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 contributes to inflammatory tongue pain via extracellular signalregulated kinase signaling in the trigeminal spinal subnucleus caudalis and upper cervical spinal cord
[paragraph_crop] => Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 contributes to inflammatory tongue pain via extracellular [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2012-11-27 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[919] => Array
(
[id] => 919
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/hydrogen-rich-saline-activated-autophagy-via-hif-1-pathways-in-neuropathic-pain-model-n919
[title] => Hydrogen-rich saline activated autophagy via HIF-1α pathways in neuropathic pain model
[paragraph_crop] => Hydrogen-rich saline activated autophagy via HIF-1α pathways in neuropathic pain model
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2012-10-26 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[34] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 34
[title] => Douleurs spontanées
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-spontanées
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[1367] => Array
(
[id] => 1367
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/validation-of-the-simplified-uvb-model-to-assess-the-pharmacodynamics-of-analgesics-in-healthy-human-volunteers-n1367
[title] => Validation of the simplified UVB model to assess the pharmacodynamics of analgesics in healthy human volunteers
[paragraph_crop] => Validation of the simplified UVB model to assess the pharmacodynamics of analgesics in healthy [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2012-05-05 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[355] => Array
(
[id] => 355
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/a-randomized--controlled-trial-validates-a-peripheral-supra-additive-antihyperalgesic-effect-of-a-paracetamolketorolac-combination---n355
[title] => A Randomized- Controlled Trial Validates a Peripheral Supra-Additive Antihyperalgesic Effect of a Paracetamol–Ketorolac Combination-
[paragraph_crop] => A Randomized, Controlled Trial Validates a Peripheral Supra-Additive Antihyperalgesic Effect [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2011-11-06 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[95] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 95
[title] => Pharmacologie
[link_rewrite] => Pharmacologie
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[1366] => Array
(
[id] => 1366
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/characteristics-of-the-neuropathy-induced-by-thoracotomy--a-4-month-follow-up-study-with-psychophysical-examination-n1366
[title] => Characteristics of the neuropathy induced by thoracotomy- a 4 month follow-up study with psychophysical examination
[paragraph_crop] => Characteristics of the neuropathy induced by thoracotomy- a 4 month follow-up study with [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2011-08-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[33] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 33
[title] => Douleurs post-opératoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-post-opératoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[337] => Array
(
[id] => 337
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/bidirectional-integrative-regulation-of-cav1-2-calcium-channel-by-microrna-mir-103--role-in-pain--n337
[title] => Bidirectional integrative regulation of Cav1-2 calcium channel by microRNA miR-103- role in pain-
[paragraph_crop] => Bidirectional integrative regulation of Cav1.2 calcium channel by microRNA miR-103: role in pain.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2011-07-29 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[331] => Array
(
[id] => 331
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/intrinsic-membrane-properties-of-spinal-dorsal-horn-neurones-modulate-nociceptive-information-processing-in-vivo---n331
[title] => Intrinsic membrane properties of spinal dorsal horn neurones modulate nociceptive information processing in vivo-
[paragraph_crop] => Intrinsic membrane properties of spinal dorsal horn neurones modulate nociceptive information [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2011-06-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[322] => Array
(
[id] => 322
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/biocompatibility-of-chronically-implanted-transverse-intrafascicular-multichannel-electrode--time--in-the-rat-sciatic-nerve---n322
[title] => Biocompatibility of Chronically Implanted Transverse Intrafascicular Multichannel Electrode -TIME- in the Rat Sciatic Nerve-
[paragraph_crop] => Biocompatibility of Chronically Implanted Transverse Intrafascicular Multichannel Electrode [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2011-05-12 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Domaines de recherche divers
[link_rewrite] => Domaines-de-recherche-divers
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[312] => Array
(
[id] => 312
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/passive-and-active-exercise-improve-regeneration-and-muscle-reinnervation-after-peripheral-nerve-injury-in-the-rat---n312
[title] => Passive and active exercise improve regeneration and muscle reinnervation after peripheral nerve injury in the rat-
[paragraph_crop] => Passive and active exercise improve regeneration and muscle reinnervation after peripheral [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2011-04-08 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[294] => Array
(
[id] => 294
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/longitudinal-study-of-wind-up-responses-after-graded-spinal-cord-injuries-in-the-adult-rat---n294
[title] => Longitudinal study of wind-up responses after graded spinal cord injuries in the adult rat-
[paragraph_crop] => Longitudinal study of wind-up responses after graded spinal cord injuries in the adult rat.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2011-02-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[263] => Array
(
[id] => 263
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/analgesic-properties-of-calcium-phosphate-apatite-loaded-with-bupivacaine-on-postoperative-pain---n263
[title] => Analgesic properties of calcium phosphate apatite loaded with bupivacaine on postoperative pain-
[paragraph_crop] => Analgesic properties of calcium phosphate apatite loaded with bupivacaine on postoperative pain.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2010-07-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[33] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 33
[title] => Douleurs post-opératoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-post-opératoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[247] => Array
(
[id] => 247
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/knockdown-of-l-calcium-channel-subtypes--differential-effects-in-neuropathic-pain--n247
[title] => Knockdown of L Calcium Channel Subtypes- Differential Effects in Neuropathic Pain-
[paragraph_crop] => Knockdown of L Calcium Channel Subtypes: Differential Effects in Neuropathic Pain.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2010-01-20 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[232] => Array
(
[id] => 232
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/electrical-stimulation-combined-with-exercise-increase-axonal-regeneration-after-peripheral-nerve-injury--n232
[title] => Electrical stimulation combined with exercise increase axonal regeneration after peripheral nerve injury-
[paragraph_crop] => Electrical stimulation combined with exercise increase axonal regeneration after peripheral [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2009-09-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[220] => Array
(
[id] => 220
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/nociceptive-responses-and-spinal-plastic-changes-of-afferent-c-fibers-in-three-neuropathic-pain-models-induced-by-sciatic-nerve-injury-in-the-rat--n220
[title] => Nociceptive responses and spinal plastic changes of afferent C-fibers in three neuropathic pain models induced by sciatic nerve injury in the rat-
[paragraph_crop] => Nociceptive responses and spinal plastic changes of afferent C-fibers in three neuropathic [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2009-05-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[192] => Array
(
[id] => 192
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/antinociceptive-and-anti-allodynic-effects-of-oral-pl37--a-complete-inhibitor-of-enkephalin-catabolizing-enzymes--in-a-rat-model-of-peripheral-neuropathic-pain-induced-by-vincristine--n192
[title] => Antinociceptive and anti-allodynic effects of oral PL37- a complete inhibitor of enkephalin-catabolizing enzymes- in a rat model of peripheral neuropathic pain induced by vincristine-
[paragraph_crop] => Antinociceptive and anti-allodynic effects of oral PL37, a complete inhibitor of [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2008-12-14 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[48] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 48
[title] => Perception du chaud et du froid
[link_rewrite] => Perception-du-chaud-et-du-froid
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[13] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 13
[title] => Système sensoriel
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-sensoriel
)
)
)
[134] => Array
(
[id] => 134
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/motor-cortex-rtms-in-chronic-neuropathic-pain--pain-relief-is-associated-with-thermal-sensory-perception-improvement--n134
[title] => Motor cortex rTMS in chronic neuropathic pain- pain relief is associated with thermal sensory perception improvement-
[paragraph_crop] => Motor cortex rTMS in chronic neuropathic pain: pain relief is associated with thermal sensory [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2008-09-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[48] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 48
[title] => Perception du chaud et du froid
[link_rewrite] => Perception-du-chaud-et-du-froid
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[13] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 13
[title] => Système sensoriel
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-sensoriel
)
)
)
[167] => Array
(
[id] => 167
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/acetaminophen-reinforces-descending-inhibitory-pain-pathways--n167
[title] => Acetaminophen Reinforces Descending Inhibitory Pain Pathways-
[paragraph_crop] => Acetaminophen Reinforces Descending Inhibitory Pain Pathways.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2008-07-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[40] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 40
[title] => Accidents ischémiques transitoires (AIT)
[link_rewrite] => Accidents-ischemiques-transitoires-AIT
)
[95] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 95
[title] => Pharmacologie
[link_rewrite] => Pharmacologie
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
[159] => Array
(
[id] => 159
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/immediate-electrical-stimulation-enhances-regeneration-and-reinnervation-and-modulates-spinal-plastic-changes-after-sciatic-nerve-injury-and-repair--n159
[title] => Immediate electrical stimulation enhances regeneration and reinnervation and modulates spinal plastic changes after sciatic nerve injury and repair-
[paragraph_crop] => Immediate electrical stimulation enhances regeneration and reinnervation and modulates spinal [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2008-05-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[38] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 38
[title] => Régénération nerveuse
[link_rewrite] => Regenération-nerveuse
)
[11] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 11
[title] => Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
[link_rewrite] => Systeme-Nerveux-Central-SNC
)
)
)
[1368] => Array
(
[id] => 1368
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/cutaneous-amitriptyline-in-human-volunteers--differential-effects-on-the-components-of-sensory-information-n1368
[title] => Cutaneous Amitriptyline in Human Volunteers- Differential Effects on the Components of Sensory Information
[paragraph_crop] => Cutaneous Amitriptyline in Human Volunteers- Differential Effects on the Components of Sensory [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2008-04-01 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[76] => Array
(
[id] => 76
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/hyperalgesia-induced-by-cutaneous-freeze-injury-for-testing-analgesics-in-healthy-volunteers--n76
[title] => Hyperalgesia induced by cutaneous freeze injury for testing analgesics in healthy volunteers-
[paragraph_crop] => Hyperalgesia induced by cutaneous freeze injury for testing analgesics in healthy volunteers.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2006-04-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[58] => Array
(
[id] => 58
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/the-novel-analgesic--f-13640--produces-intra--and-postoperative-analgesia-in-a-rat-model-of-surgical-pain--n58
[title] => The novel analgesic- F 13640- produces intra- and postoperative analgesia in a rat model of surgical pain-
[paragraph_crop] => The novel analgesic, F 13640, produces intra- and postoperative analgesia in a rat model of [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2005-10-31 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[36] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 36
[title] => Allodynie mécanique & Hyperalgésie
[link_rewrite] => Allodynie-mecanique-Hyperalgesie
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[33] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 33
[title] => Douleurs post-opératoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-post-opératoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[20] => Array
(
[id] => 20
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/up-regulation-of-fatty-acid-metabolizing-enzymes-mrna-in-rat-spinal-cord-during-persistent-peripheral-local-inflammation--n20
[title] => Up-regulation of fatty acid metabolizing-enzymes mRNA in rat spinal cord during persistent peripheral local inflammation-
[paragraph_crop] => Up-regulation of fatty acid metabolizing-enzymes mRNA in rat spinal cord during persistent [...]
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2003-10-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Douleurs chroniques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-chroniques
)
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Douleurs inflammatoires
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-inflammatoires
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
)
[9] => Array
(
[id] => 9
[url] => https://bioseb.com/fr/news/large-amplitude-5-ht1a-receptor-activation--a-new-mechanism-of-profound--central-analgesia--n9
[title] => Large-amplitude 5-HT1A receptor activation- a new mechanism of profound- central analgesia-
[paragraph_crop] => Large-amplitude 5-HT1A receptor activation: a new mechanism of profound, central analgesia.
[image_presente] =>
[date] => 2002-11-30 00:00:00
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[27] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 27
[title] => Douleurs générales
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-generales
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[95] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 95
[title] => Pharmacologie
[link_rewrite] => Pharmacologie
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
)
)
)
1Nombre de publications:
En tant que version électronique du classique esthésiomètre à filaments de Von Frey, la dernière évolution de...
Nouvelles cage de contention modulables ROBUSTES pour maintenir doucement les rongeurs (rats et souris) durant les...
Une solution économique et versatile pour les situations nécessitant des tests sensoriels quantitatifs (QST): construit...
check_circle
check_circle