Authors
HJ Park, CK Lee, SH Song, JH Yun, A Lee, HJ Park
Lab
Department of Food and Nutrition, Yuhan University, 590 Gyeongin-ro, Bucheon-si, Gyeonggi-do, 14780, Korea
Journal
Food Science and Biotechnology
Abstract
This study was performed to investigate the effects of highly bioavailable curcumin as Theracurmin (TC) in rats with monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)-induced osteoarthritis (OA). Seventy-seven male Wistar rats were divided into six groups: normal, negative control (MIA only), positive control (Cerebrex), and three experimental groups treated with 500, 1300, or 2600 mg/kg of TC for 5 weeks. MIA injection-induced OA caused 30% weight-bearing imbalance whereas weight bearing imbalance was significantly improved in the TC groups. Mankin scores revealed TC treatment had significantly ameliorated cartilage damage and chondrocyte decrease. The expressions of nitrotyrosine, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, phosphorylated nuclear factor kappa B cells, and cleaved caspase-3 were markedly increased in rat with MIA-induced OA, but the TC-treated groups exhibited a significant reduction in the number of immunoreactive cells in a dose-dependent manner. In conclusion, administration of TC contributes to the anti-arthritic effect in rat with MIA-induced OA.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
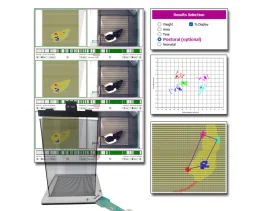
Electronic Von Frey 4 (BIO-EVF4)
Source :
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10068-019-00679-5#auth-6

 Douleur - Allodynie/Hyperalgésie Thermique
Douleur - Allodynie/Hyperalgésie Thermique Douleur - Spontanée - Déficit de Posture
Douleur - Spontanée - Déficit de Posture Douleur - Allodynie/Hyperalgésie Mécanique
Douleur - Allodynie/Hyperalgésie Mécanique Apprentissage/Mémoire - Attention - Addiction
Apprentissage/Mémoire - Attention - Addiction Physiologie & Recherche Respiratoire
Physiologie & Recherche Respiratoire


































 Douleur
Douleur Système Nerveux Central (SNC)
Système Nerveux Central (SNC)  Neurodégénérescence
Neurodégénérescence Système sensoriel
Système sensoriel Système moteur
Système moteur Troubles de l'humeur
Troubles de l'humeur Autres pathologies
Autres pathologies Système musculaire
Système musculaire Articulations
Articulations Métabolisme
Métabolisme Thématiques transversales
Thématiques transversales Congrès & Meetings
Congrès & Meetings 