Neuropathic pain perplexes a large population of patients with various diseases. Inflammation plays a key role in the physiopathology of...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 943
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2017-11-27 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:12
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[prim_key] => 1850
[id_lang] => 2
[title] => MiR-145 ameliorates neuropathic pain via inhibiting inflammatory responses and m
[paragraph] => MiR-145 ameliorates neuropathic pain via inhibiting inflammatory responses and mTOR signaling pathway by targeting Akt3 in a rat model
[content] => Authors
J Shia, K Jiang, Z Li
Lab
Department of Anesthesiology, Guizhou Provincial Peoples Hospital, China
Journal
Nueroscience Research
Abstract
Neuropathic pain perplexes a large population of patients with various diseases. Inflammation plays a key role in the physiopathology of neuropathic pain. Anti-inflammatory can be a promising strategy to treat neuropathic pain. We generated a chronic constriction injury rat model to mimic neuropathic pain by ligating the left ischiadic nerves of rats. Then we performed intrathecal injection of miR-145 mimics to treat these rats for seven consecutive days. Pain behavior tests including mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia, pro-inflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-_, interleukin (IL)-1_ and IL-6 were analyzed. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction and immunoblotting were performed to detect the changes of signaling pathway after miR-145 mimic treatment. Targeting of Akt3 by miR-145 was studied by dual-luciferase reporter gene assays. MiR-145 mimics injection significantly mollified both mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia in rats, and down-regulated secretion of TNF-_, IL-1_ and IL-6. We confirmed that miR-145 directly targeted Akt3, inhibiting NF-_B and mTOR downstream genes in rat dorsal root ganglia. MiR-145 can mollify neuropathic pain in a chronic constriction injury rat model by reducing inflammation and ion channel overexpression through Akt3/mTOR and Akt3/NF-_B signaling pathways.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Von Frey Filaments (Bio-VF-M)
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168010217303851
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => mir-145-ameliorates-neuropathic-pain-via-inhibiting-inflammatory-responses-and-mtor-signaling-pathway-by-targeting-akt3-in-a-rat-model
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 944
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 943
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => MiR-145 ameliorates neuropathic pain via inhibiting inflammatory responses and mTOR signaling [...]
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[577] => Array
(
[name] => Filaments de Von Frey
[description_short] => Jeu de 20 filaments basé sur le jeu de monofilaments de Wemmes Weinstein - filament rétractable pour protéger celui-ci et faciliter le transport


[thumb] => 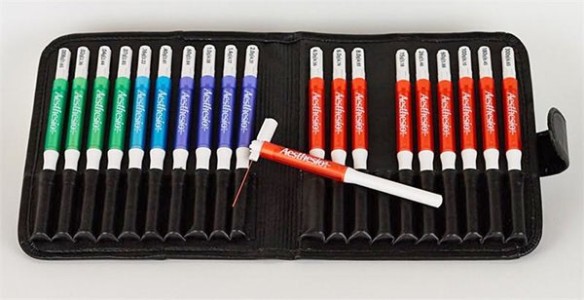 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-allodyniehyperalgesie-mecanique/577-von-frey-filaments.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-allodyniehyperalgesie-mecanique/577-von-frey-filaments.html
)
)
)
1 En lire plus 
