Neurotensin (NT) exerts naloxone-insensitive antinociceptive action through its binding to both NTS1 and NTS2 receptors and NT analogs provide...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 1269
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2020-05-01 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:12
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[ishero] => 0
[prim_key] => 2496
[id_lang] => 2
[title] => Pain relief devoid of opioid side effects following central action of a silylate
[paragraph] => Pain relief devoid of opioid side effects following central action of a silylated neurotensin analog
[content] => Authors
P T
Lab
Department of Pharmacology-Physiology, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universit
Journal
arXiv
Abstract
Neurotensin (NT) exerts naloxone-insensitive antinociceptive action through its binding to both NTS1 and NTS2 receptors and NT analogs provide stronger pain relief than morphine on a molecular basis. Here, we examined the analgesic/adverse effect profile of a new NT(8-13) derivative denoted JMV2009, in which the Pro10 residue was substituted by a silicon-containing unnatural amino acid silaproline. We first report the synthesis and in vitro characterization (receptor-binding affinity, functional activity and stability) of JMV2009. We next examined its analgesic activity in a battery of acute, tonic and chronic pain models. We finally evaluated its ability to induce adverse effects associated with chronic opioid use, such as constipation and analgesic tolerance or related to NTS1 activation, like hypothermia. In in vitro assays, JMV2009 exhibited high binding affinity for both NTS1 and NTS2, improved proteolytic resistance as well as agonistic activities similar to NT, inducing sustained activation of p42/p44 MAPK and receptor internalization. Intrathecal injection of JMV2009 produced ose-dependent antinociceptive responses in the tail-flick test and almost completely abolished the nociceptive related behaviors induced by chemical somatic and visceral noxious stimuli. Likewise, increasing doses of JMV2009 significantly reduced tactile allodynia and weight bearing deficits in nerve injured rats. Importantly, repeated agonist treatment did not result in the development of analgesic tolerance. Furthermore, JMV2009 did not cause constipation and was ineffective in inducing hypothermia. These findings suggest that NT drugs can act as an effective opioid-free medication for the management of pain or can serve as adjuvant analgesics to reduce the opioid adverse effects.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 (BIO-DWB-DUAL)
Keywords/Topics
Douleurs neuropathiques; Douleur
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/2005/2005.01887.pdf
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => pain-relief-devoid-of-opioid-side-effects-following-central-action-of-a-silylated-neurotensin-analog
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 1152
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 1269
[categories] => Array
(
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Douleur
[link_rewrite] => Douleur
)
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => Pain relief devoid of opioid side effects following central action of a silylated neurotensin analog
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[1216] => Array
(
[name] => Distribution Pondérale Dynamique 2.0
[description_short] =>
Un système permettant l'analyse de la posture des animaux par la répartition du poids sur chacune des 4 pattes. Le DWB est un test unique dans l'étude de nombreux modèles de douleurs, principalement non évoquée , neuropathique ou encore inflammatoire ainsi que pour les études sur l'osthéoarthrite et divers affections du SNC.
Le nouvelle version DWB2 intègre une nouvelle interface logiciel plus simple avec gestion des listes d'animaux ainsi que de nouveaux algorithmes d'analyse automatique de la posture.


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Module Postural Additionnel
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Module Postural Additionnel
[description_short] => Étendez votre analyse grâce à des calculs posturaux et locomoteurs avancés
Le système de Distribution Pondérale Dynamique (DWB2) de BIOSEB s’enrichit avec l'ajout du Module Postural. Ce complément logiciel optionnel améliore l’analyse standard de la répartition du poids en intégrant des nouveaux calculs conçus pour l’étude de la posture, de la locomotion et de l’activité des animaux.
Développé en collaboration avec le laboratoire du Dr. Tighilet de l’Université Aix-Marseille - CNRS, le Module Postural améliore votre DWB2 en fournissant des paramètres précieux pour les recherches sur la douleur, les troubles vestibulaires et les maladies neurodégénératives.


[thumb] => 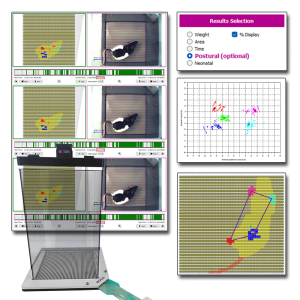 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-module-postural-additionnel.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-module-postural-additionnel.html
)
)
)
1 En lire plus 
