Despite years of research, our understanding of the mechanisms by which inflammation induces depression is still limited. As clinical data points...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 1026
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2018-04-27 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:12
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[prim_key] => 2014
[id_lang] => 2
[title] => Motivational changes that develop in a mouse model of inflammation-induced depre
[paragraph] => Motivational changes that develop in a mouse model of inflammation-induced depression are independent of indoleamine 2, 3 dioxygenase.
[content] => Authors
EG Vichaya, G Laumet, DL Christian, AJ Grossberg, DJ Estrada, CJ Heijnen, A Kavelaars, R Dantzer
Lab
Division of Internal Medicine, Department of Symptom Research, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
Journal
Neuropsychopharmacology
Abstract
Despite years of research, our understanding of the mechanisms by which inflammation induces depression is still limited. As clinical data points to a strong association between depression and motivational alterations, we sought to (1) characterize the motivational changes that are associated with inflammation in mice, and (2) determine if they depend on inflammation-induced activation of indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase-1 (IDO1). Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated or spared nerve injured (SNI) wild type (WT) and Ido1_/_ mice underwent behavioral tests of antidepressant activity (e.g., forced swim test) and motivated behavior, including assessment of (1) reward expectancy using a food-related anticipatory activity task, (2) willingness to work for reward using a progressive ratio schedule of food reinforcement, (3) effort allocation using a concurrent choice task, and (4) ability to associate environmental cues with reward using conditioned place preference. LPS- and SNI-induced deficits in behavioral tests of antidepressant activity in WT but not Ido1_/_ mice. Further, LPS decreased food related-anticipatory activity, reduced performance in the progressive ratio task, and shifted effort toward the preferred reward in the concurrent choice task. These effects were observed in both WT and Ido1_/_ mice. Finally, SNI mice developed a conditioned place preference based on relief from pain in an IDO1-independent manner. These findings demonstrate that the motivational effects of inflammation do not require IDO1. Further, they indicate that the motivational component of inflammation-induced depression is mechanistically distinct from that measured by behavioral tests of antidepressant activity.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 (BIO-DWB-DUAL)
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => https://www.nature.com/articles/s41386-018-0075-z
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => motivational-changes-that-develop-in-a-mouse-model-of-inflammation-induced-depression-are-independent-of-indoleamine-2--3-dioxygenase-
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 1062
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 1026
[categories] => Array
(
[57] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 57
[title] => Dépression
[link_rewrite] => Depression
)
[93] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 93
[title] => Inflammation
[link_rewrite] => Inflammation
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Thématiques transversales
[link_rewrite] => Thematiques-transversales
)
[15] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 15
[title] => Troubles de l'humeur
[link_rewrite] => Troubles-de-l-humeur
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => Motivational changes that develop in a mouse model of inflammation-induced depression are [...]
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[1216] => Array
(
[name] => Distribution Pondérale Dynamique 2.0
[description_short] => Un système permettant l'analyse de la posture des animaux par la répartition du poids sur chacune des 4 pattes. Le DWB est un test unique dans l'étude de nombreux modèles de douleurs, principalement non évoquée , neuropathique ou encore inflammatoire ainsi que pour les études sur l'osthéoarthrite et divers affections du SNC.
Le nouvelle version DWB2 intègre une nouvelle interface logiciel plus simple avec gestion des listes d'animaux ainsi que de nouveaux algorithmes d'analyse automatique de la posture.


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Module Postural Additionnel
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Module Postural Additionnel
[description_short] => Étendez votre analyse grâce à des calculs posturaux et locomoteurs avancés
Le système de Distribution Pondérale Dynamique (DWB2) de BIOSEB s’enrichit avec l'ajout du Module Postural. Ce complément logiciel optionnel améliore l’analyse standard de la répartition du poids en intégrant des nouveaux calculs conçus pour l’étude de la posture, de la locomotion et de l’activité des animaux.
Développé en collaboration avec le laboratoire du Dr. Tighilet de l’Université Aix-Marseille - CNRS, le Module Postural améliore votre DWB2 en fournissant des paramètres précieux pour les recherches sur la douleur, les troubles vestibulaires et les maladies neurodégénératives.


[thumb] => 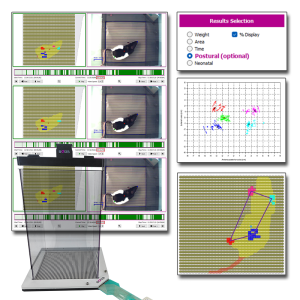 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-module-postural-additionnel.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-module-postural-additionnel.html
)
)
)
1 En lire plus 
