: Background: In the present study, we examined superoxide-mediated excitatory nociceptive transmission on at-level neuropathic pain following...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 1384
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2021-03-06 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:12
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[ishero] => 0
[prim_key] => 2967
[id_lang] => 2
[title] => The Roles of Superoxide on At-Level Spinal Cord Injury Pain in Rat
[paragraph] => The Roles of Superoxide on At-Level Spinal Cord Injury Pain in Rat
[content] => Authors
BH Lee, J Kang, HY Kim et al
Lab
Department of Physiology, College of Korean Medicine, Daegu Haany University, Daegu 42158, Korea
Journal
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Abstract
Abstract: Background: In the present study, we examined superoxide-mediated excitatory nociceptive transmission on at-level neuropathic pain following spinal thoracic 10 contusion injury (SCI) in male Sprague Dawley rats. Methods: Mechanical sensitivity at body trunk, neuronal firing activity, and expression of superoxide marker/ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs)/CamKII were mea sured in the T7/8 dorsal horn, respectively. Results: Topical treatment of superoxide donor t-BOOH (0.4 mg/kg) increased neuronal firing rates and pCamKII expression in the naïve group, whereas superoxide scavenger Tempol (1 mg/kg) and non-specific ROS scavenger PBN (3 mg/kg) decreased firing rates in the SCI group (* p < 0.05). SCI showed increases of iGluRs-mediated neuronal firing rates and pCamKII expression (* p < 0.05); however, t-BOOH treatment did not show significant changes in the naïve group. The mechanical sensitivity at the body trunk in the SCI group (6.2 ± 0.5) was attenuated by CamKII inhibitor KN-93 (50 microg, 3.9 ± 0.4) or Tempol (1 mg, 4 ± 0.4) treatment (* p < 0.05). In addition, the level of superoxide marker Dhet showed significant increase in SCI rats compared to the sham group (11.7 ± 1.7 vs. 6.6 ± 1.5, * p < 0.05). Conclusions: Superoxide and the pCamKII pathway contribute to chronic at-level neuropathic pain without involvement of iGluRs following SCI.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Von Frey Filaments (Bio-VF-M)
Keywords/Topics
Douleurs neuropathiques
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => http://scholar.google.fr/scholar_url?url=https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/5/2672/pdf&hl=fr&sa=X&d=7785722274921199362&ei=KdNLYK2-HoeUmAHdtouICA&scisig=AAGBfm3owU84Tmf2UazK57gmJOEdXptZIw&nossl=1&oi=scholaralrt&hist=dLa5yvYAAAAJ:2499066874814899551:AAGBfm0
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => the-roles-of-superoxide-on-at-level-spinal-cord-injury-pain-in-rat-
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 930
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 1384
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => The Roles of Superoxide on At-Level Spinal Cord Injury Pain in Rat
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[577] => Array
(
[name] => Filaments de Von Frey
[description_short] =>
Jeu de 20 filaments basé sur le jeu de monofilaments de Wemmes Weinstein - filament rétractable pour protéger celui-ci et faciliter le transport


[thumb] => 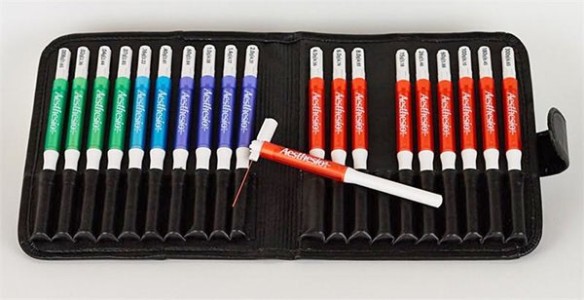 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-allodyniehyperalgesie-mecanique/577-von-frey-filaments.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-allodyniehyperalgesie-mecanique/577-von-frey-filaments.html
)
)
)
1 En lire plus 
