Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which are isolated from adipose tissue (AD-MSCs), umbilical cord (UC-MSCs), or bone marrow, have therapeutic...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 1508
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2022-02-14 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:13
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[ishero] => 0
[prim_key] => 3218
[id_lang] => 2
[title] => Intravenous administration of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose
[paragraph] => Intravenous administration of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue and umbilical cord improves neuropathic pain via suppression of neuronal damage and anti-inflammatory actions in rats
[content] => Authors
K Miyano, M Ikehata, K Ohshima et al
Lab
The Jikei University School of Medicine, Nishishimbashi, Minato-ku, Tokyo, Japan
Journal
PLOS One
Abstract
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which are isolated from adipose tissue (AD-MSCs), umbilical cord (UC-MSCs), or bone marrow, have therapeutic potential including anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities. It was recently reported that MSCs are also effective as a therapeutic treatment for neuropathic pain, although the underlying mechanisms have yet to be resolved. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the effects of human AD- and UC-MSCs on neuropathic pain and its mechanisms using rat models of partial sciatic nerve ligation (PSNL). AD- or UC-MSCs were intravenously administered 4 days after PSNL. Antinociceptive effects were then evaluated using the von Frey and weight-bearing tests. We found that, 3Ð9 days after the administration of AD- or UC-MSCs to PSNL-exposed rats, both the mechanical threshold and differences in weight-bearing of the right and left hind paws were significantly improved. To reveal the potential underlying antinociceptive mechanisms of MSCs, the levels of activation transcription factor 3- and ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1-positive cells were measured by immunohistochemical analysis. AD- and UC-MSCs significantly decreased the levels of these proteins that were induced by PSNL in the dorsal root ganglia. Additionally, UC-MSC significantly improved the PSNL-induced decrease in the myelin basic protein level in the sciatic nerve, indicating that UC-MSC reversed demyelination of the sciatic nerve produced by PSNL. These data suggest that AD- and UC-MSCs may help in the recovery of neuropathic pain via the different regulation; AD-MSCs exhibited their effects via suppressed neuronal damage and anti-inflammatory actions, while UC-MSCs exhibited their effects via suppressed neuronal damage, anti-inflammatory actions and remyelination.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 (BIO-DWB-DUAL)
Keywords/Topics
Douleurs neuropathiques
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0262892
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => intravenous-administration-of-human-mesenchymal-stem-cells-derived-from-adipose-tissue-and-umbilical-cord-improves-neuropathic-pain-via-suppression-of-neuronal-damage-and-anti-inflammatory-actions-in-rats
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 836
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 1508
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Douleurs neuropathiques
[link_rewrite] => Douleurs-neuropathiques
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => Intravenous administration of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue and [...]
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[1216] => Array
(
[name] => Distribution Pondérale Dynamique 2.0
[description_short] =>
Un système permettant l'analyse de la posture des animaux par la répartition du poids sur chacune des 4 pattes. Le DWB est un test unique dans l'étude de nombreux modèles de douleurs, principalement non évoquée , neuropathique ou encore inflammatoire ainsi que pour les études sur l'osthéoarthrite et divers affections du SNC.
Le nouvelle version DWB2 intègre une nouvelle interface logiciel plus simple avec gestion des listes d'animaux ainsi que de nouveaux algorithmes d'analyse automatique de la posture.


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Module Postural Additionnel
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Module Postural Additionnel
[description_short] => Étendez votre analyse grâce à des calculs posturaux et locomoteurs avancés
Le système de Distribution Pondérale Dynamique (DWB2) de BIOSEB s’enrichit avec l'ajout du Module Postural. Ce complément logiciel optionnel améliore l’analyse standard de la répartition du poids en intégrant des nouveaux calculs conçus pour l’étude de la posture, de la locomotion et de l’activité des animaux.
Développé en collaboration avec le laboratoire du Dr. Tighilet de l’Université Aix-Marseille - CNRS, le Module Postural améliore votre DWB2 en fournissant des paramètres précieux pour les recherches sur la douleur, les troubles vestibulaires et les maladies neurodégénératives.


[thumb] => 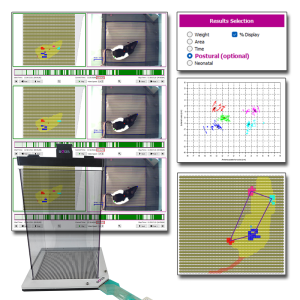 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-module-postural-additionnel.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-module-postural-additionnel.html
)
)
)
1 En lire plus 
