The assessment of articular nociception in experimental animals is a challenge because available methods are limited and subject to investigator...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 815
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2015-10-29 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:12
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[prim_key] => 1594
[id_lang] => 2
[title] => Dynamic weight bearing is an efficient and predictable method for evaluation of
[paragraph] => Dynamic weight bearing is an efficient and predictable method for evaluation of arthritic nociception and its pathophysiological mechanisms in mice
[content] => Authors
Andreza U. Quadros, Larissa G. Pinto, Miriam M. Fonseca, Ricardo Kusuda, Fernando Q. Cunha & Thiago M. Cunha
Lab
Department of Pharmacology, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Brazil
Journal
Scientific Reports
Abstract
The assessment of articular nociception in experimental animals is a challenge because available methods are limited and subject to investigator influence. In an attempt to solve this problem, the purpose of this study was to establish the use of dynamic weight bearing (DWB) as a new device for evaluating joint nociception in an experimental model of antigen-induced arthritis (AIA) in mice. AIA was induced in Balb/c and C57BL/6 mice, and joint nociception was evaluated by DWB. Western Blotting and real-time PCR were used to determine protein and mRNA expression, respectively. DWB detected a dose- and time-dependent increase in joint nociception during AIA and was able to detect the dose-response effects of different classes of analgesics. Using DWB, it was possible to evaluate the participation of spinal glial cells (microglia and astrocytes) and cytokines (IL-1β and TNFα) for the genesis of joint nociception during AIA. In conclusion, the present results indicated that DWB is an effective, objective and predictable test to study both the pathophysiological mechanisms involved in arthritic nociception in mice and for evaluating novel analgesic drugs against arthritis.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 (BIO-DWB-DUAL)
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => http://www.nature.com/articles/srep14648
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => dynamic-weight-bearing-is-an-efficient-and-predictable-method-for-evaluation-of-arthritic-nociception-and-its-pathophysiological-mechanisms-in-mice
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 1013
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 815
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthrite & Arthrose
[link_rewrite] => Arthrite-Arthrose
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Articulations
[link_rewrite] => Articulations
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => Dynamic weight bearing is an efficient and predictable method for evaluation of arthritic [...]
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[1216] => Array
(
[name] => Distribution Pondérale Dynamique 2.0
[description_short] => Un système permettant l'analyse de la posture des animaux par la répartition du poids sur chacune des 4 pattes. Le DWB est un test unique dans l'étude de nombreux modèles de douleurs, principalement non évoquée , neuropathique ou encore inflammatoire ainsi que pour les études sur l'osthéoarthrite et divers affections du SNC.
Le nouvelle version DWB2 intègre une nouvelle interface logiciel plus simple avec gestion des listes d'animaux ainsi que de nouveaux algorithmes d'analyse automatique de la posture.


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Module Postural Additionnel
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Module Postural Additionnel
[description_short] => Étendez votre analyse grâce à des calculs posturaux et locomoteurs avancés
Le système de Distribution Pondérale Dynamique (DWB2) de BIOSEB s’enrichit avec l'ajout du Module Postural. Ce complément logiciel optionnel améliore l’analyse standard de la répartition du poids en intégrant des nouveaux calculs conçus pour l’étude de la posture, de la locomotion et de l’activité des animaux.
Développé en collaboration avec le laboratoire du Dr. Tighilet de l’Université Aix-Marseille - CNRS, le Module Postural améliore votre DWB2 en fournissant des paramètres précieux pour les recherches sur la douleur, les troubles vestibulaires et les maladies neurodégénératives.


[thumb] => 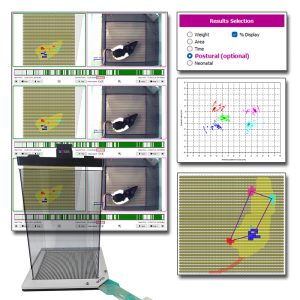 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-module-postural-additionnel.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/fr/douleur-spontanee-deficit-de-posture/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-module-postural-additionnel.html
)
)
)
1 En lire plus 
