Authors
Hideki Kashiwadani, Yuichi Kanmura, Tomoyuki Kuwaki
Lab
Kagoshima University, Kagoshima, Japan
Journal
PLOS One
Abstract
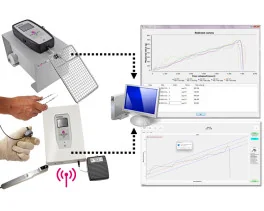
In order to investigate the basic physiological mechanisms of pain and the anti-nociceptive effects of analgesics, development of pain assays in mice is critical due to the advances of genetic manipulation techniques. The von Frey hairs/Semmes-Weinstein monofilaments test (von Frey test) has long been applied to examine mechanical nociception in mice. Though the von Frey test is a well-established and standardized method, it is inappropriate to assess a rapid change in the nociceptive threshold because voluntary resting/sleeping states are necessary to examine the response. In this study, we assessed the effectiveness of calibrated forceps to determine the mechanical nociceptive threshold in mice. Repeated daily measurements of the threshold over 5 days indicated that the device obtained stable and reliable values. Furthermore, repeated measurements with 5 minute intervals revealed that the device detected the rapid change of the threshold induced by remifentanil, a shortacting_-receptor agonist. These results indicate that the calibrated forceps are well-suited for measuring the mechanical nociceptive threshold in mice, and are useful in assessing the effects of short-acting analgesics on mechanical nociception.
BIOSEB Instruments Used:
Rodent pincher - analgesia meter (BIO-RP-M)

 Pain - Thermal Allodynia / Hyperalgesia
Pain - Thermal Allodynia / Hyperalgesia Pain - Spontaneous Pain - Postural Deficit
Pain - Spontaneous Pain - Postural Deficit Pain - Mechanical Allodynia / Hyperalgesia
Pain - Mechanical Allodynia / Hyperalgesia Learning/Memory - Attention - Addiction
Learning/Memory - Attention - Addiction Physiology & Respiratory Research
Physiology & Respiratory Research



































 Pain
Pain Central Nervous System (CNS)
Central Nervous System (CNS) Neurodegeneration
Neurodegeneration Sensory system
Sensory system Motor control
Motor control Mood Disorders
Mood Disorders Other disorders
Other disorders Muscular system
Muscular system Joints
Joints Metabolism
Metabolism Cross-disciplinary subjects
Cross-disciplinary subjects CONFERENCES & MEETINGS
CONFERENCES & MEETINGS 