Unilateral vestibular lesions induce a vestibular syndrome, which recovers over time due to vestibular compensation. The therapeutic effect of...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 1497
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2022-02-16 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:13
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[ishero] => 0
[prim_key] => 3160
[id_lang] => 1
[title] => L-Thyroxine Improves Vestibular Compensation in a Rat Model of Acute Peripheral
[paragraph] => L-Thyroxine Improves Vestibular Compensation in a Rat Model of Acute Peripheral Vestibulopathy: Cellular and Behavioral Aspects
[content] => Authors
G Rastoldo, E Marouane, N El-Mahmoudi et al
Lab
Aix Marseille Universite-CNRS, Laboratoire de Neurosciences Cognitives, Marseille, France
Journal
Cells
Abstract
Unilateral vestibular lesions induce a vestibular syndrome, which recovers over time due to vestibular compensation. The therapeutic effect of L-Thyroxine (L-T4) on vestibular compensation was investigated by behavioral testing and immunohistochemical analysis in a rat model of unilateral vestibular neurectomy (UVN). We demonstrated that a short-term L-T4 treatment reduced the vestibular syndrome and significantly promoted vestibular compensation. Thyroid hormone receptors (TRalpha and TRbeta) and type II iodothyronine deiodinase (DIO2) were present in the vestibular nuclei (VN), supporting a local action of L-T4. We confirmed the T4-induced metabolic effects by demonstrating an increase in the number of cytochrome oxidase-labeled neurons in the VN three days after the lesion. L-T4 treatment modulated glial reaction by decreasing both microglia and oligodendrocytes in the deafferented VN three days after UVN and increased cell proliferation. Survival of newly generated cells in the deafferented vestibular nuclei was not affected, but microglial rather than neuronal differentiation was favored by L-T4 treatment.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 (BIO-DWB-DUAL)
Keywords/Topics
Vestibular system
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11040684
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => l-thyroxine-improves-vestibular-compensation-in-a-rat-model-of-acute-peripheral-vestibulopathy---cellular-and-behavioral-aspects
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 953
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 1497
[categories] => Array
(
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
[49] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 49
[title] => Vestibular system
[link_rewrite] => Vestibular-system
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => L-Thyroxine Improves Vestibular Compensation in a Rat Model of Acute Peripheral [...]
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[1216] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0
[description_short] =>
The advanced version of our Dynamic Weight Bearing Test for rodents (rats and mice) allows for faster paw identification, based on a video solution taking advantage of the most advanced algorithms of morphologic analysis, weight distribution and postural changes in dynamic conditions. An efficient and advanced alternative to traditional incapacitance tests (i.e. the paw pressure test or the force plate test) for assessing pain sensitivity in your research on analgesia, hyperalgesia and nociception involving rats and mice, including work on osteoarthritis, bone cancer, analgesic substances, Parkinson disease, allodynia...


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Postural Module [Add-on]
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Postural Module [Add-on]
[description_short] => Expand Your Analysis with Advanced Postural and Locomotor Calculations
BIOSEB’s renowned Dynamic Weight Bearing (DWB2) system is now more powerful than ever with the addition of the Postural Module. This optional software upgrade extends standard weight-bearing analysis by integrating unique calculations designed to quantify subtle aspects of postural balance, locomotor patterns, and compensatory behaviors.
Developed in collaboration with Dr. Tighilet’s lab from Aix Marseille Université-CNRS, the Postural Module improves your DWB2, providing valuable endpoints for studies on pain, neurology, vestibular dysfunction, and neurodegenerative disorders.


[thumb] => 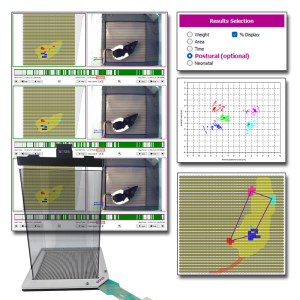 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-add-on-postural-module.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-add-on-postural-module.html
)
)
)
1 Read more 
