Authors
C Sprenger, K Koda, D de la Mora, T Yamada, H Mano et al
Lab
Computational and Biological Learning Laboratory, Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge, Trumpington Street, Cambridge CB2 1PZ, UK
Journal
Brain and Neuroscience Advances
Abstract
A cardinal feature of persistent pain that follows injury is a general suppression of behaviour, in which motivation is inhibited in a way that promotes energy conservation and recuperation. Across species, the anterior cingulate cortex is associated with the motivational aspects of phasic pain, but whether it mediates motivational functions in persistent pain is less clear. Using burrowing behaviour as an marker of non-specific motivated behaviour in rodents, we studied the suppression of burrowing following painful confirmatory factor analysis or control injection into the right knee joint of 30 rats (14 with pain) and examined associated neural connectivity with ultra-high-field resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging. We found that connectivity between anterior cingulate cortex and subcortical structures including hypothalamic/preoptic nuclei and the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis correlated with the reduction in burrowing behaviour observed following the pain manipulation. In summary, the findings implicate anterior cingulate cortex connectivity as a correlate of the motivational aspect of persistent pain in rodents.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
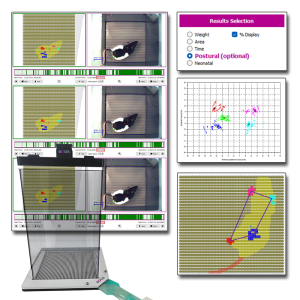
Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 (BIO-DWB-DUAL)
Source :

 Pain - Thermal Allodynia / Hyperalgesia
Pain - Thermal Allodynia / Hyperalgesia Pain - Spontaneous Pain - Postural Deficit
Pain - Spontaneous Pain - Postural Deficit Pain - Mechanical Allodynia / Hyperalgesia
Pain - Mechanical Allodynia / Hyperalgesia Learning/Memory - Attention - Addiction
Learning/Memory - Attention - Addiction Physiology & Respiratory Research
Physiology & Respiratory Research











![Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Postural Module [Add-on]](https://bioseb.com/733-home_default/dynamic-weight-bearing-20-add-on-postural-module.jpg)
























 Pain
Pain Central Nervous System (CNS)
Central Nervous System (CNS) Neurodegeneration
Neurodegeneration Sensory system
Sensory system Motor control
Motor control Mood Disorders
Mood Disorders Other disorders
Other disorders Muscular system
Muscular system Joints
Joints Metabolism
Metabolism Cross-disciplinary subjects
Cross-disciplinary subjects CONFERENCES & MEETINGS
CONFERENCES & MEETINGS