Authors
Salamone, Paula C., Enmalm, Adam, Kaldewaij, Reinoud, Ã…man, Marie, Medley, Charlotte, Pietrzak, Michal, Olausson, HÃ¥kan, Capusan, Andrea Johansson, Boehme, Rebecca
Lab
Journal
Molecular Psychiatry
Abstract
Psychosis is often characterized by disturbances in the sense of self, with patients frequently misattributing self-produced sensations to external sources. While somatic hallucinations and misperceptions are common, the underlying disruptions in basic bodily self-processing remain unclear. We aimed to investigate processing of self-evoked sensations, including touch and interoception, in psychosis using a multimodal, multi-method approach. This case-control-study included a total of 70 participants (35 patients diagnosed with psychotic disorders, 35 age- and sex-matched controls). Participants performed self-/other-touch-tasks and interoceptive assessments during functional MRI, evoked potentials measurements, and/or behavioral and psychophysical tests. Primary outcomes included neural and behavioral responses to self- and externally-generated sensations (touch and heartbeat). Brain activation, spinal evoked responses, heartbeat perception and processing (evoked responses), and behavioral measures were analyzed, with preregistered hypotheses. Patients demonstrated heightened right superior temporal gyrus activation during self-touch. Tactile self-other distinction impairments were evident at the spinal cord level. Behaviorally, patients showed reduced differentiation in tactile thresholds for self- vs. other-touch. Interoceptive impairments included diminished cortical responses to heartbeat signals, lower interoceptive accuracy (heartbeat detection), and reduced self-reported interoceptive sensitivity. These findings reveal pervasive sensory and self-related disturbances in psychotic disorders. Impairments in differentiating self- and externally-evoked responses, detectable as early as the spinal cord level, may contribute to higher-order symptoms of psychosis.
Keywords/Topics
Neuroscience; Schizophrenia
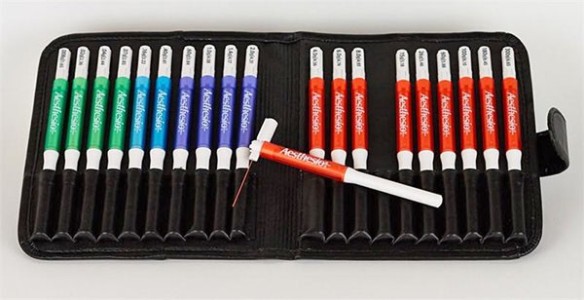
BIOSEB Instruments Used:
Von Frey Filaments (BIO-VF-M)
Source :

 Pain - Thermal Allodynia / Hyperalgesia
Pain - Thermal Allodynia / Hyperalgesia Pain - Spontaneous Pain - Postural Deficit
Pain - Spontaneous Pain - Postural Deficit Pain - Mechanical Allodynia / Hyperalgesia
Pain - Mechanical Allodynia / Hyperalgesia Learning/Memory - Attention - Addiction
Learning/Memory - Attention - Addiction Physiology & Respiratory Research
Physiology & Respiratory Research











![Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Postural Module [Add-on]](https://bioseb.com/733-home_default/dynamic-weight-bearing-20-add-on-postural-module.jpg)
























 Pain
Pain Central Nervous System (CNS)
Central Nervous System (CNS) Neurodegeneration
Neurodegeneration Sensory system
Sensory system Motor control
Motor control Mood Disorders
Mood Disorders Other disorders
Other disorders Muscular system
Muscular system Joints
Joints Metabolism
Metabolism Cross-disciplinary subjects
Cross-disciplinary subjects CONFERENCES & MEETINGS
CONFERENCES & MEETINGS