Inflammatory pain impacts adversely on the quality of life of patients, often resulting in motor disabilities. Therefore, we studied the effect of...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 396
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2012-04-30 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:11
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[ishero] => 0
[prim_key] => 787
[id_lang] => 1
[title] => Inflammation-induced decrease in voluntary wheel running in mice- a nonreflexive
[paragraph] => Inflammation-induced decrease in voluntary wheel running in mice: a nonreflexive test for evaluating inflammatory pain and analgesia.
[content] => Authors
E. Cobos, N. Ghasemlou, D. Araldi, D. Segal, K. Duong et al.
Lab
Children's Hospital Boston, F.M. Kirby Neurobiology Center, Boston, USA.
Journal
Pain
Abstract
Inflammatory pain impacts adversely on the quality of life of patients, often resulting in motor disabilities. Therefore, we studied the effect of peripheral inflammation induced by intraplantar administration of complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) in mice on a particular form of voluntary locomotion, wheel running, as an index of mobility impairment produced by pain. The distance traveled over 1 hour of free access to activity wheels decreased significantly in response to hind paw inflammation, peaking 24 hours after CFA administration. Recovery of voluntary wheel running by day 3 correlated with the ability to support weight on the inflamed limb. Inflammation-induced mechanical hypersensitivity, measured with von Frey hairs, lasted considerably longer than the impaired voluntary wheel running and is not driving; therefore, the change in voluntary behavior. The CFA-induced decrease in voluntary wheel running was dose-dependently reversed by subcutaneous administration of antiinflammatory and analgesic drugs, including naproxen (10-80 mg/kg), ibuprofen (2.5-20mg/kg), diclofenac (1.25-10mg/kg), celecoxib (2.5-20mg/kg), prednisolone (0.62-5mg/kg), and morphine (0.06-0.5mg/kg), all at much lower doses than reported in most rodent models. Furthermore, the doses that induced recovery in voluntary wheel running did not reduce CFA-induced mechanical allodynia, indicating a greater sensitivity of the former as a surrogate measure of inflammatory pain. We conclude that monitoring changes in voluntary wheel running in mice during peripheral inflammation is a simple, observer-independent objective measure of functional changes produced by inflammation, likely more aligned to the global level of pain than reflexive measures, and much more sensitive to analgesic drug effects.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Spontaneous activity wheels (BIO-ACTIVW-M),Plethysmometer (BX-PLETHY),Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 (BIO-DWB-DUAL)
Keywords/Topics
Inflammatory pain; Pain
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => http://www.painjournalonline.com/article/S0304-3959%2812%2900028-0/abstract
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => inflammation-induced-decrease-in-voluntary-wheel-running-in-mice--a-nonreflexive-test-for-evaluating-inflammatory-pain-and-analgesia-
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 1498
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 396
[categories] => Array
(
[28] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 28
[title] => Inflammatory pain
[link_rewrite] => Inflammatory-pain
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Pain
[link_rewrite] => Pain
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => Inflammation-induced decrease in voluntary wheel running in mice: a nonreflexive test for [...]
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[40] => Array
(
[name] => Premium spontaneous activity wheels
[description_short] =>
The BIOSEB Spontaneous Activity Wheel offers an effective solution for quantifying rodent voluntary activity within their home cage environment. The embedded electronics provide a wide range of measurements including wheel revolutions, average/min/max speed, acceleration, utilization time, access events, and more. The Premium model expands on these standard features, enabling animal filming and task complexity enhancement by removing bars. Beyond neuromuscular diseases, this tool also facilitates the study of neurodegenerative disorders, including Parkinson's, Huntington's, and ALS.


[thumb] => 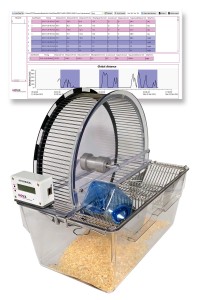 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/activity-motor-control-coordination/40-spontaneous-activity-wheels.html
)
[565] => Array
(
[name] => Plethysmometer
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/activity-motor-control-coordination/40-spontaneous-activity-wheels.html
)
[565] => Array
(
[name] => Plethysmometer
[description_short] => Highly useful tool in the measurement of small volume changes


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-mechanical-allodynia-hyperalgesia/565-plethysmometer.html
)
[1216] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-mechanical-allodynia-hyperalgesia/565-plethysmometer.html
)
[1216] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0
[description_short] => The advanced version of our Dynamic Weight Bearing Test for rodents (rats and mice) allows for faster paw identification, based on a video solution taking advantage of the most advanced algorithms of morphologic analysis, weight distribution and postural changes in dynamic conditions. An efficient and advanced alternative to traditional incapacitance tests (i.e. the paw pressure test or the force plate test) for assessing pain sensitivity in your research on analgesia, hyperalgesia and nociception involving rats and mice, including work on osteoarthritis, bone cancer, analgesic substances, Parkinson disease, allodynia...


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1875] => Array
(
[name] => Basic spontaneous activity wheels
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1875] => Array
(
[name] => Basic spontaneous activity wheels
[description_short] => The BIOSEB Spontaneous Activity Wheel is an easy way to quantify rodent voluntary activity in their home cage environment. The embedded electronics perform a wide range of measurements, including: wheel revolutions, average/min/max speed, acceleration, utilization time, number of access events among others . A useful tool for studies on Drug Screening, Phenotyping Circadian Rhythms, and Neuromuscular Diseases; now with a software-independent LCD display and redesigned software controlling up to 64 wheels!


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/activity-motor-control-coordination/1875-spontaneous-activity-wheels.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Postural Module [Add-on]
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/activity-motor-control-coordination/1875-spontaneous-activity-wheels.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Postural Module [Add-on]
[description_short] => Expand Your Analysis with Advanced Postural and Locomotor Calculations
BIOSEB’s renowned Dynamic Weight Bearing (DWB2) system is now more powerful than ever with the addition of the Postural Module. This optional software upgrade extends standard weight-bearing analysis by integrating unique calculations designed to quantify subtle aspects of postural balance, locomotor patterns, and compensatory behaviors.
Developed in collaboration with Dr. Tighilet’s lab from Aix Marseille Université-CNRS, the Postural Module improves your DWB2, providing valuable endpoints for studies on pain, neurology, vestibular dysfunction, and neurodegenerative disorders.


[thumb] => 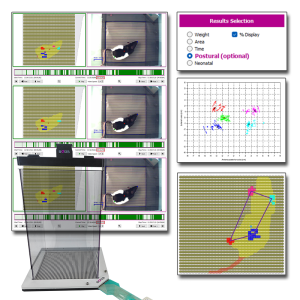 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-add-on-postural-module.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-add-on-postural-module.html
)
)
)
1 Read more 
