The pharmacological inhibition of anandamide (AEA) hydrolysis by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) attenuates pain in animal models of...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 725
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2015-05-01 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:12
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[ishero] => 0
[prim_key] => 1417
[id_lang] => 1
[title] => A multi-target approach for pain treatment- dual inhibition of fatty acid amide
[paragraph] => A multi-target approach for pain treatment: dual inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase and TRPV1 in a rat model of osteoarthritis
[content] => Authors
Malek N, Mrugala M, Makuch W, Kolosowska N, Przewlocka B, Binkowski M, Czaja M, Morera E, Di Marzo V, Starowicz K.
Lab
Laboratory of Pain Pathophysiology, Institute of Pharmacology, Polish Academy of Sciences, Krakow, Poland
Journal
Pain
Abstract
The pharmacological inhibition of anandamide (AEA) hydrolysis by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) attenuates pain in animal models of osteoarthritis (OA) but has failed in clinical trials. This may have occurred because AEA also activates transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1), which contributes to pain development. Therefore, we investigated the effectiveness of the dual FAAH-TRPV1 blocker OMDM-198 in an MIA-model of osteoarthritic pain. We first investigated the MIA-induced model of OA by (1) characterizing the pain phenotype and degenerative changes within the joint using X-ray microtomography and (2) evaluating nerve injury and inflammation marker (ATF-3 and IL-6) expression in the lumbar dorsal root ganglia of osteoarthritic rats and differences in gene and protein expression of the cannabinoid CB1 receptors FAAH and TRPV1. Furthermore, we compared OMDM-198 with compounds acting exclusively on FAAH or TRPV1. Osteoarthritis was accompanied by the fragmentation of bone microstructure and destroyed cartilage. An increase of the mRNA levels of ATF3 and IL-6 and an upregulation of AEA receptors and FAAH in the dorsal root ganglia were observed. OMDM-198 showed antihyperalgesic effects in the OA model, which were comparable with those of a selective TRPV1 antagonist, SB-366,791, and a selective FAAH inhibitor, URB-597. The effect of OMDM-198 was attenuated by the CB1 receptor antagonist, AM-251, and by the nonpungent TRPV1 agonist, olvanil, suggesting its action as an indirect CB1 agonist and TRPV1 antagonist. These results suggest an innovative strategy for the treatment of OA, which may yield more satisfactory results than those obtained so far with selective FAAH inhibitors in human OA.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 (BIO-DWB-DUAL)
Keywords/Topics
Arthritis & Osteoarthritis; Joints
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25719612
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => a-multi-target-approach-for-pain-treatment--dual-inhibition-of-fatty-acid-amide-hydrolase-and-trpv1-in-a-rat-model-of-osteoarthritis
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 1359
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 725
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthritis & Osteoarthritis
[link_rewrite] => Arthritis-Osteoarthritis
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Joints
[link_rewrite] => Joints
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => A multi-target approach for pain treatment: dual inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase and [...]
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[1216] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0
[description_short] =>
The advanced version of our Dynamic Weight Bearing Test for rodents (rats and mice) allows for faster paw identification, based on a video solution taking advantage of the most advanced algorithms of morphologic analysis, weight distribution and postural changes in dynamic conditions. An efficient and advanced alternative to traditional incapacitance tests (i.e. the paw pressure test or the force plate test) for assessing pain sensitivity in your research on analgesia, hyperalgesia and nociception involving rats and mice, including work on osteoarthritis, bone cancer, analgesic substances, Parkinson disease, allodynia...


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Postural Module [Add-on]
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Postural Module [Add-on]
[description_short] => Expand Your Analysis with Advanced Postural and Locomotor Calculations
BIOSEB’s renowned Dynamic Weight Bearing (DWB2) system is now more powerful than ever with the addition of the Postural Module. This optional software upgrade extends standard weight-bearing analysis by integrating unique calculations designed to quantify subtle aspects of postural balance, locomotor patterns, and compensatory behaviors.
Developed in collaboration with Dr. Tighilet’s lab from Aix Marseille Université-CNRS, the Postural Module improves your DWB2, providing valuable endpoints for studies on pain, neurology, vestibular dysfunction, and neurodegenerative disorders.


[thumb] => 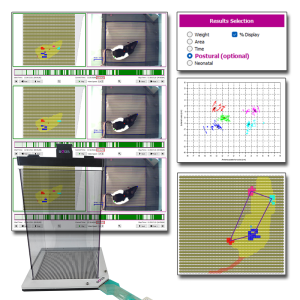 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-add-on-postural-module.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-add-on-postural-module.html
)
)
)
1 Read more 
