Chronic joint pain such as mechanical allodynia is the most debilitating symptom of arthritis, yet effective therapies are lacking. We identify the...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 1054
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2018-08-08 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:12
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[ishero] => 0
[prim_key] => 2069
[id_lang] => 1
[title] => Microglial pannexin-1 channel activation is a spinal determinant of joint pain
[paragraph] => Microglial pannexin-1 channel activation is a spinal determinant of joint pain
[content] => Authors
M Mousseau, NE Burma, K Yeop Lee, H Leduc-Pessah, et al.
Lab
Comparative Biology and Experimental Medicine, University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
Journal
Science Advances
Abstract
Chronic joint pain such as mechanical allodynia is the most debilitating symptom of arthritis, yet effective therapies are lacking. We identify the pannexin-1 (Panx1) channel as a therapeutic target for alleviating mechanical allodynia, a cardinal sign of arthritis. In rats, joint pain caused by intra-articular injection of monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) was associated with spinal adenosine 5_-triphosphate (ATP) release and a microglia-specific up-regulation of P2X7 receptors (P2X7Rs). Blockade of P2X7R or ablation of spinal microglia prevented and reversed mechanical allodynia. P2X7Rs drive Panx1 channel activation, and in rats with mechanical allodynia, Panx1 function was increased in spinal microglia. Specifically, microglial Panx1-mediated release of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1_ (IL-1_) induced mechanical allodynia in the MIA-injected hindlimb. Intrathecal administration of the Panx1-blocking peptide 10panx suppressed the aberrant discharge of spinal laminae I-II neurons evoked by innocuous mechanical hindpaw stimulation in arthritic rats. Furthermore, mice with a microglia-specific genetic deletion of Panx1 were protected from developing mechanical allodynia. Treatment with probenecid, a clinically used broad-spectrum Panx1 blocker, resulted in a striking attenuation of MIA-induced mechanical allodynia and normalized responses in the dynamic weight-bearing test, without affecting acute nociception. Probenecid reversal of mechanical allodynia was also observed in rats 13 weeks after anterior cruciate ligament transection, a model of posttraumatic osteoarthritis. Thus, Panx1-targeted therapy is a new mechanistic approach for alleviating joint pain.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 (BIO-DWB-DUAL)
Keywords/Topics
Arthritis & Osteoarthritis; Joints
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => http://advances.sciencemag.org/content/4/8/eaas9846
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => microglial-pannexin-1-channel-activation-is-a-spinal-determinant-of-joint-pain
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 1438
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 1054
[categories] => Array
(
[70] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 70
[title] => Arthritis & Osteoarthritis
[link_rewrite] => Arthritis-Osteoarthritis
)
[21] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 21
[title] => Joints
[link_rewrite] => Joints
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => Microglial pannexin-1 channel activation is a spinal determinant of joint pain
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[1216] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0
[description_short] =>
The advanced version of our Dynamic Weight Bearing Test for rodents (rats and mice) allows for faster paw identification, based on a video solution taking advantage of the most advanced algorithms of morphologic analysis, weight distribution and postural changes in dynamic conditions. An efficient and advanced alternative to traditional incapacitance tests (i.e. the paw pressure test or the force plate test) for assessing pain sensitivity in your research on analgesia, hyperalgesia and nociception involving rats and mice, including work on osteoarthritis, bone cancer, analgesic substances, Parkinson disease, allodynia...


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Postural Module [Add-on]
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Postural Module [Add-on]
[description_short] => Expand Your Analysis with Advanced Postural and Locomotor Calculations
BIOSEB’s renowned Dynamic Weight Bearing (DWB2) system is now more powerful than ever with the addition of the Postural Module. This optional software upgrade extends standard weight-bearing analysis by integrating unique calculations designed to quantify subtle aspects of postural balance, locomotor patterns, and compensatory behaviors.
Developed in collaboration with Dr. Tighilet’s lab from Aix Marseille Université-CNRS, the Postural Module improves your DWB2, providing valuable endpoints for studies on pain, neurology, vestibular dysfunction, and neurodegenerative disorders.


[thumb] => 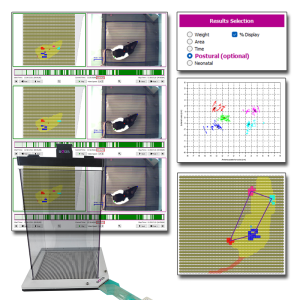 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-add-on-postural-module.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-add-on-postural-module.html
)
)
)
1 Read more 
