We explored the molecular and behavioral effects of a perineural Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated inflammatory priming on the development and...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 1072
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2018-10-01 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:12
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[ishero] => 0
[prim_key] => 2105
[id_lang] => 1
[title] => Lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammatory priming potentiates painful post-trauma
[paragraph] => Lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammatory priming potentiates painful post-traumatic trigeminal neuropathy
[content] => Authors
Y Boucher, N Moreau, A Mauborgne, W Dieb
Lab
Laboratoire de Neurobiologie Orofaciale, UFR d'Odontologie, Université Paris Diderot, Paris, France.
Journal
Physiology & Behavior
Abstract
We explored the molecular and behavioral effects of a perineural Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated inflammatory priming on the development and maintenance of painful post-traumatic trigeminal neuropathy (PPTTN) following infra-orbital nerve chronic constriction injury (CCI-IoN) in rats. Rats were pretreated with repetitive perineural injections in the vicinity of the IoN of either LPS or vehicle (Vhcl) before being submitted to CCI-IoN. Orofacial pain-like behaviors (response to Von Frey Filament testing and spontaneous isolated face grooming) were measured during the period of LPS injections (three weeks) and following CCI-IoN surgery (two weeks). Local LPS administration induced an early pain-like behavior (i.e. an increase in spontaneous pain [SP] or mechanical static allodynia [MSA]) in both conditions, and following CCI-IoN, MSA and SP developed earlier and more severely in LPS-pretreated rats than in the control group. Ipsilateral increases of key neuropathic pain mRNA markers in the IoN parenchyma, trigeminal ganglia (TG) and spinal trigeminal nucleus caudalis (Sp5C) were observed in CCI-IoN injured animals as compared to controls. Although no significant molecular differences could be observed within the IoN parenchyma between LPS and Vhcl-pretreated animals, a significant increase of key inflammatory cytokine Interleukin 1 beta (IL___1_) could be found in the TG of LPS-pretreated CCI-injured animals versus controls. Finally, a higher increase of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in ipsilateral Sp5C of LPS-pretreated animals was observed as compared to Sp5C of Vhcl-pretreated animals. These results suggest a key role of inflammatory priming in the development and maintenance of PPTTN implicating IL-1_/iNOS-dependent central sensitization mechanisms.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Von Frey Filaments (Bio-VF-M)
Keywords/Topics
Neuropathic pain; Pain
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0031938418303718#!
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => lipopolysaccharide-mediated-inflammatory-priming-potentiates-painful-post-traumatic-trigeminal-neuropathy
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 1233
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 1072
[categories] => Array
(
[29] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 29
[title] => Neuropathic pain
[link_rewrite] => Neuropathic-pain
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Pain
[link_rewrite] => Pain
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => Lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammatory priming potentiates painful post-traumatic trigeminal [...]
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[577] => Array
(
[name] => Von Frey Filaments
[description_short] =>
A set of 20 monofilaments based on the Semmes Weinstein monofilament set - featuring retractable filaments to protect the filament and allow the investigator to carry a few around in a pocket


[thumb] => 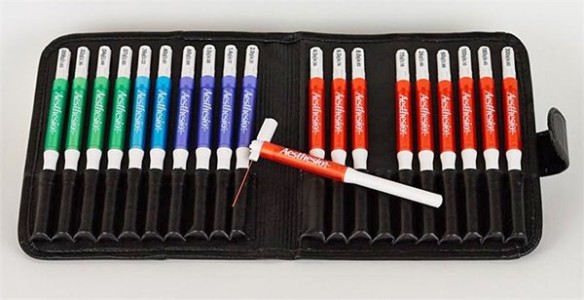 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-mechanical-allodynia-hyperalgesia/577-von-frey-filaments.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-mechanical-allodynia-hyperalgesia/577-von-frey-filaments.html
)
)
)
1 Read more 
