Breast cancer cells release the signalling molecule glutamate via the system xC_ antiporter, which is upregulated to exchange extracellular cystine...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 1028
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2018-05-05 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:12
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[ishero] => 0
[prim_key] => 2017
[id_lang] => 1
[title] => Functional effects of TrkA inhibition on system xC_-mediated glutamate release a
[paragraph] => Functional effects of TrkA inhibition on system xC_-mediated glutamate release and cancer-induced bone pain
[content] => Authors
T Miladinovic, RG Ungard, K Linher-Melville, S Popovic, S Popovic, G Singh
Lab
McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
Journal
Molecular Pain
Abstract
Breast cancer cells release the signalling molecule glutamate via the system xC_ antiporter, which is upregulated to exchange extracellular cystine for intracellular glutamate to protect against oxidative stress. Here, we demonstrate that this antiporter is functionally influenced by the actions of the neurotrophin nerve growth factor on its cognate receptor tyrosine kinase, TrkA, and that inhibiting this complex may reduce cancer-induced bone pain via its downstream actions on xCT, the functional subunit of system xC_. We have characterized the effects of the selective TrkA inhibitor AG879 on system xC_ activity in murine 4T1 and human MDA-MB-231 mammary carcinoma cells, as well as its effects on nociception in our validated immunocompetent mouse model of cancer-induced bone pain, in which BALB/c mice are intrafemorally inoculated with 4T1 murine carcinoma cells. AG879 decreased functional system xC_ activity, as measured by cystine uptake and glutamate release, and inhibited nociceptive and physiologically relevant responses in tumour-bearing animals. Cumulatively, these data suggest that the activation of TrkA by nerve growth factor may have functional implications on system xC_-mediated cancer pain. System xC_-mediated TrkA activation therefore presents a promising target for therapeutic intervention in cancer pain treatment.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 (BIO-DWB-DUAL)
Keywords/Topics
Chronic pain; Cancer; Pain; Cross-disciplinary subjects
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/1744806918776467
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => functional-effects-of-trka-inhibition-on-system-xc-mediated-glutamate-release-and-cancer-induced-bone-pain
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 1455
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 1028
[categories] => Array
(
[90] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 90
[title] => Cancer
[link_rewrite] => Cancer
)
[30] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 30
[title] => Chronic pain
[link_rewrite] => Chronic-pain
)
[24] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 24
[title] => Cross-disciplinary subjects
[link_rewrite] => Cross-disciplinary-subjects-
)
[10] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 10
[title] => Pain
[link_rewrite] => Pain
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => Functional effects of TrkA inhibition on system xC_-mediated glutamate release and [...]
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[1216] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0
[description_short] =>
The advanced version of our Dynamic Weight Bearing Test for rodents (rats and mice) allows for faster paw identification, based on a video solution taking advantage of the most advanced algorithms of morphologic analysis, weight distribution and postural changes in dynamic conditions. An efficient and advanced alternative to traditional incapacitance tests (i.e. the paw pressure test or the force plate test) for assessing pain sensitivity in your research on analgesia, hyperalgesia and nociception involving rats and mice, including work on osteoarthritis, bone cancer, analgesic substances, Parkinson disease, allodynia...


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Postural Module [Add-on]
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Postural Module [Add-on]
[description_short] => Expand Your Analysis with Advanced Postural and Locomotor Calculations
BIOSEB’s renowned Dynamic Weight Bearing (DWB2) system is now more powerful than ever with the addition of the Postural Module. This optional software upgrade extends standard weight-bearing analysis by integrating unique calculations designed to quantify subtle aspects of postural balance, locomotor patterns, and compensatory behaviors.
Developed in collaboration with Dr. Tighilet’s lab from Aix Marseille Université-CNRS, the Postural Module improves your DWB2, providing valuable endpoints for studies on pain, neurology, vestibular dysfunction, and neurodegenerative disorders.


[thumb] => 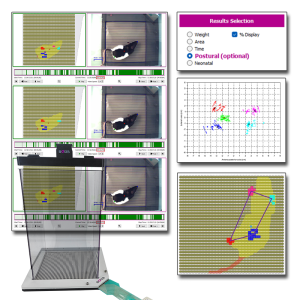 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-add-on-postural-module.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-add-on-postural-module.html
)
)
)
1 Read more 
