Deficits in the basal ganglia pathways modulating cortical motor activity underlie both Parkinson disease (PD) and Huntington disease (HD)....
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 858
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2016-04-07 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:12
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[ishero] => 0
[prim_key] => 1679
[id_lang] => 1
[title] => Biallelic Mutations in PDE10A Lead to Loss of Striatal PDE10A and a Hyperkinetic
[paragraph] => Biallelic Mutations in PDE10A Lead to Loss of Striatal PDE10A and a Hyperkinetic Movement Disorder with Onset in Infancy
[content] => Authors
Diggle CP, Sukoff Rizzo SJ, Popiolek M, Hinttala R, Schülke JP et al.
Lab
School of Medicine, University of Leeds, Leeds LS9 7TF, UK.
Journal
Am J Hum Genet.
Abstract
Deficits in the basal ganglia pathways modulating cortical motor activity underlie both Parkinson disease (PD) and Huntington disease (HD). Phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A) is enriched in the striatum, and animal data suggest that it is a key regulator of this circuitry. Here, we report on germline PDE10A mutations in eight individuals from two families affected by a hyperkinetic movement disorder due to homozygous mutations c.320A>G (p.Tyr107Cys) and c.346G>C (p.Ala116Pro). Both mutations lead to a reduction in PDE10A levels in recombinant cellular systems, and critically, positron-emission-tomography (PET) studies with a specific PDE10A ligand confirmed that the p.Tyr107Cys variant also reduced striatal PDE10A levels in one of the affected individuals. A knock-in mouse model carrying the homologous p.Tyr97Cys variant had decreased striatal PDE10A and also displayed motor abnormalities. Striatal preparations from this animal had an impaired capacity to degrade cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and a blunted pharmacological response to PDE10A inhibitors. These observations highlight the critical role of PDE10A in motor control across species.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 (BIO-DWB-DUAL)
Keywords/Topics
Miscellaneous research domains
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27058446
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => biallelic-mutations-in-pde10a-lead-to-loss-of-striatal-pde10a-and-a-hyperkinetic-movement-disorder-with-onset-in-infancy
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 1327
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 858
[categories] => Array
(
[26] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 26
[title] => Miscellaneous research domains
[link_rewrite] => Miscellaneous-research-domains
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => Biallelic Mutations in PDE10A Lead to Loss of Striatal PDE10A and a Hyperkinetic Movement [...]
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[1216] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0
[description_short] =>
The advanced version of our Dynamic Weight Bearing Test for rodents (rats and mice) allows for faster paw identification, based on a video solution taking advantage of the most advanced algorithms of morphologic analysis, weight distribution and postural changes in dynamic conditions. An efficient and advanced alternative to traditional incapacitance tests (i.e. the paw pressure test or the force plate test) for assessing pain sensitivity in your research on analgesia, hyperalgesia and nociception involving rats and mice, including work on osteoarthritis, bone cancer, analgesic substances, Parkinson disease, allodynia...


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Postural Module [Add-on]
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1216-dynamic-weight-bearing-20.html
)
[1877] => Array
(
[name] => Dynamic Weight Bearing 2.0 – Postural Module [Add-on]
[description_short] => Expand Your Analysis with Advanced Postural and Locomotor Calculations
BIOSEB’s renowned Dynamic Weight Bearing (DWB2) system is now more powerful than ever with the addition of the Postural Module. This optional software upgrade extends standard weight-bearing analysis by integrating unique calculations designed to quantify subtle aspects of postural balance, locomotor patterns, and compensatory behaviors.
Developed in collaboration with Dr. Tighilet’s lab from Aix Marseille Université-CNRS, the Postural Module improves your DWB2, providing valuable endpoints for studies on pain, neurology, vestibular dysfunction, and neurodegenerative disorders.


[thumb] => 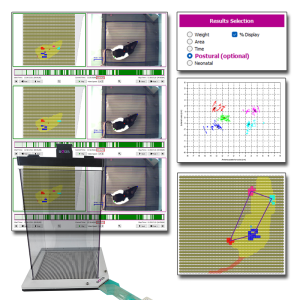 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-add-on-postural-module.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/pain-spontaneous-pain-postural-deficit/1877-dynamic-weight-bearing-20-add-on-postural-module.html
)
)
)
1 Read more 
