The genetic regulation and physiological impact of most lipid species are unexplored. Here, we profiled 129 plasma lipid species across 49 strains...
Array
(
[id_prestablog_news] => 1030
[id_shop] => 1
[date] => 2018-06-27 00:00:00
[date_modification] => 2024-02-09 14:15:12
[langues] => ["1","2"]
[actif] => 1
[slide] => 0
[url_redirect] =>
[average_rating] =>
[number_rating] =>
[author_id] => 1
[featured] => 0
[ishero] => 0
[prim_key] => 2021
[id_lang] => 1
[title] => Genetic Regulation of Plasma Lipid Species and Their Association with Metabolic
[paragraph] => Genetic Regulation of Plasma Lipid Species and Their Association with Metabolic Phenotypes
[content] => Authors
P Jha, MT McDevitt, R Gupta, PM Quiros, EG Williams, K Gariani, MB Sleiman, L Diserens, A Jochem, A Ulbrich, JJ Coon, J Auwerx, DJ Pagliarini
Lab
Laboratory of Integrative and Systems Physiology, École Polytchnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Lausanne 1015, Switzerland
Journal
Cell Systems
Abstract
The genetic regulation and physiological impact of most lipid species are unexplored. Here, we profiled 129 plasma lipid species across 49 strains of the BXD mouse genetic reference population fed either chow or a high-fat diet. By integrating these data with genomics and phenomics datasets, we elucidated genes by environment (diet) interactions that regulate systemic metabolism. We found quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for _94% of the lipids measured. Several QTLs harbored genes associated with blood lipid levels and abnormal lipid metabolism in human genome-wide association studies. Lipid species from different classes provided signatures of metabolic health, including seven plasma triglyceride species that associated with either healthy or fatty liver. This observation was further validated in an independent mouse model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and in plasma from NAFLD patients. This work provides a resource to identify plausible genes regulating the measured lipid species and their association with metabolic traits.
BIOSEB Instruments Used
Spontaneous activity wheels (BIO-ACTIVW-M)
Keywords/Topics
Cell metabolism; Food intake / Nutrition; Metabolism
[meta_description] =>
[meta_keywords] => https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405471218301972#!
[meta_title] =>
[link_rewrite] => genetic-regulation-of-plasma-lipid-species-and-their-association-with-metabolic-phenotypes
[actif_langue] => 1
[read] => 1213
[count_comments] => 0
[id] => 1030
[categories] => Array
(
[78] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 78
[title] => Cell metabolism
[link_rewrite] => Cell-metabolism
)
[82] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 82
[title] => Food intake / Nutrition
[link_rewrite] => Food-intake-Nutrition
)
[23] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 23
[title] => Metabolism
[link_rewrite] => Metabolism
)
[2] => Array
(
[id_prestablog_categorie] => 2
[title] => Publications
[link_rewrite] => publications
)
)
[authors] =>
[paragraph_crop] => Genetic Regulation of Plasma Lipid Species and Their Association with Metabolic Phenotypes
[link_for_unique] => 1
[products_liaison] => Array
(
[40] => Array
(
[name] => Premium spontaneous activity wheels
[description_short] =>
The BIOSEB Spontaneous Activity Wheel offers an effective solution for quantifying rodent voluntary activity within their home cage environment. The embedded electronics provide a wide range of measurements including wheel revolutions, average/min/max speed, acceleration, utilization time, access events, and more. The Premium model expands on these standard features, enabling animal filming and task complexity enhancement by removing bars. Beyond neuromuscular diseases, this tool also facilitates the study of neurodegenerative disorders, including Parkinson's, Huntington's, and ALS.


[thumb] => 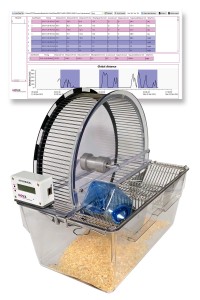 [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/activity-motor-control-coordination/40-spontaneous-activity-wheels.html
)
[1875] => Array
(
[name] => Basic spontaneous activity wheels
[description_short] =>
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/activity-motor-control-coordination/40-spontaneous-activity-wheels.html
)
[1875] => Array
(
[name] => Basic spontaneous activity wheels
[description_short] => The BIOSEB Spontaneous Activity Wheel is an easy way to quantify rodent voluntary activity in their home cage environment. The embedded electronics perform a wide range of measurements, including: wheel revolutions, average/min/max speed, acceleration, utilization time, number of access events among others . A useful tool for studies on Drug Screening, Phenotyping Circadian Rhythms, and Neuromuscular Diseases; now with a software-independent LCD display and redesigned software controlling up to 64 wheels!


[thumb] =>  [img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/activity-motor-control-coordination/1875-spontaneous-activity-wheels.html
)
)
)
1
[img_empty] => /var/www/vhosts/de3310.ispfr.net/bioseb2024/modules/prestablog/views/img/product_link_white.jpg
[image_presente] => 1
[link] => https://bioseb.com/en/activity-motor-control-coordination/1875-spontaneous-activity-wheels.html
)
)
)
1 Read more 
